The range of sports supplements on the sports nutrition market is constantly expanding. And the fact that bodybuilders, weightlifters and crossfitters seemed like a fairy tale yesterday is now becoming a reality. For example, for a long time it was believed that it was impossible to change the source of energy production without salbutamol, clenbuterol or ephedrine. This fact has been challenged with the advent of l-carnitine.
General information
We will understand the most important points related to l-carnitine - what it is, what functions it performs and how the substance affects the process of losing weight.
Definition
Carnitine is a substance similar in properties to the group of B vitamins, but unlike them, it is independently synthesized in the human body in the liver and kidneys. The prefix “L” means that the substance carnitine is of natural origin. Levocarnitine and L-carnitine are different variations of the same term.
The most important characteristics
Levocarnitine is an amino acid that has three important functions that directly affect athletic performance:
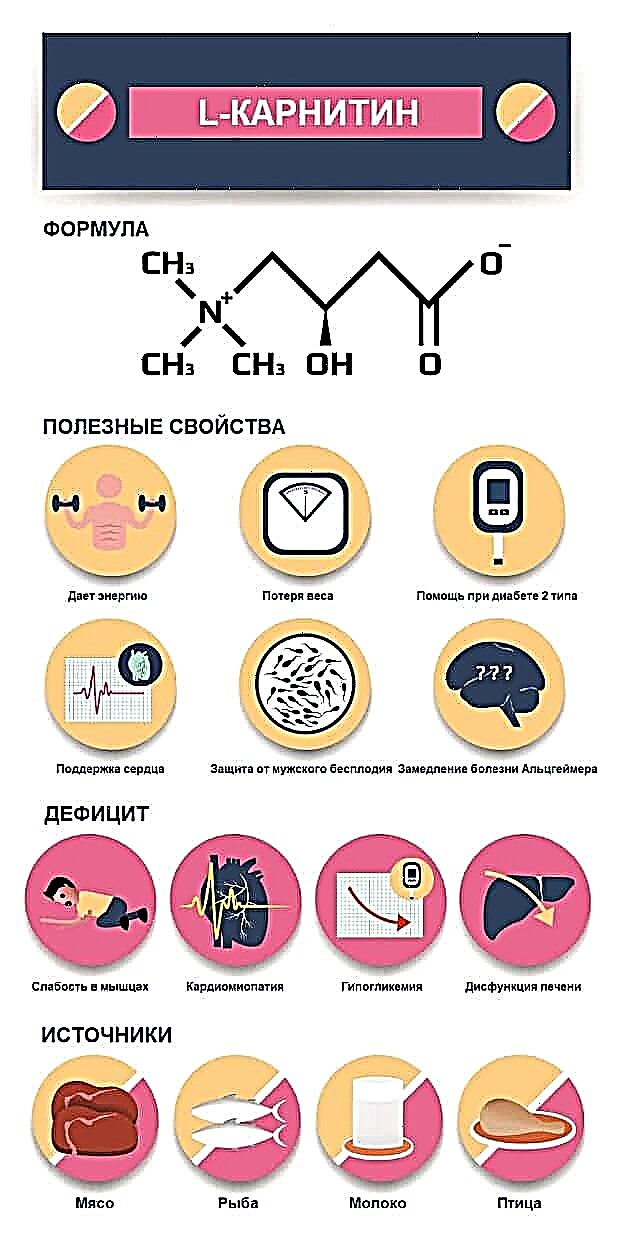
- Levocarnitine is a nutrient, a kind of "vapor" that moves fatty acids from the blood to the mitochondria. Thanks to this agent, fatty acids can be used as energy. If you want to use fat as fuel and do it as efficiently as possible, you will definitely need levocarnitine.
- L-Carnitine improves endurance by inhibiting the build-up of lactic acid, one of the main causes of fatigue.
- Levocarnitine reduces the build-up of metabolic waste during exercise. This feature allows for increased workload during exercise and improved recovery from exercise.
© nipadahong - stock.adobe.com
Importance in the process of losing weight
L-Carnitine for weight loss may be especially important during periods of intense competition preparation as it lowers post-workout lactic acid levels and improves performance. It maintains muscle glycogen levels during exercise. An increase in oxygen consumption and a decrease in respiratory factor indicate that dietary l-carnitine stimulates lipid metabolism, allowing fatty acids to be used as an energy source.
It causes a significant decrease in postoperative plasma lactate, which is produced and used continuously under fully aerobic conditions.
Out of a control group of 10,000 people, less than 1% are hypersensitive to this nutrient - they are people with kidney problems or serious heart rhythm disturbances.
© Artemida-psy - stock.adobe.com
The use of carnitine in sports
The effectiveness of carnitine in fat burning and weight loss, although it has been proven by many studies, is almost never used in sports. The fact is that the drying methods used by professional athletes are much more effective than the effects of using carnitine, even at an increased dosage. In fact, in terms of weight loss, carnitine is a placebo: the change in the ratio of the percentage of energy distribution from lipid to glycogen tissue remains negligible.
Carnitine does not melt fat cells, but only transfers them to the mitochondria. This means that the rate at which energy is obtained from the fat cells is increased, therefore, the process of burning fat is accelerated. This factor can be used to accelerate preparations based on salbutamol, clenbuterol, ephedrine (for example, ECA), caffeine. A small dose of L-carnitine will eliminate many of the side effects of these substances.
In addition, in this case, carnitine will increase the efficiency of training, as it will more quickly provide energy from the burned fats. This in turn will significantly increase strength endurance and overall vigor during the day during drying.
But does it make sense to take l-carnitine solo? Yes, especially for CrossFit athletes. L-carnitine is a non-steroidal substance that affects the strength of the heart muscle and reduces the level of lactic acid.
From this it follows that with carnitine you can increase the heart rate threshold, while achieving it will be much more difficult. This does not mean that you can train much more intensely, but exercise will do much less damage to the cardiovascular system. In this case, carnitine acts as a means of preventing the "sports heart syndrome"
The substance will be especially useful for older athletes and people who have just started training and have not been involved in sports before.
So, there is an effect from taking carnitine, but you should not use it as a fat burner or cardio assistant without unnecessary need - it is unprofitable. In sports, carnitine is used mainly as a stabilizer of the processes of other substances and an enhancer of their effects.
Note: This does not prevent most instructors from actively pushing carnitine on the market, under the guise of a powerful fat burner. In particular, this is common in elite fitness clubs, where instructors' salaries are directly dependent on the sales of a sports bar.
Where to find carnitine
Where to find L-carnitine and why look for it? Unlike creatine (consonant in name and similar in functionality), L-carnitine is found in excess in meat products, in particular in red meat. However, in meat and generally in its natural form, carnitine is practically useless. Lipolic acid is in it in its neutral form and only if the body needs to accumulate or synthesize it will be transformed.
Eating a huge piece of steak may not be good. Due to active catabolic processes taking place in a long-term background, D-carnitine can be produced in the body, which will have an extremely detrimental effect on muscle growth, endurance and other indicators.
Therefore, it is best to take carnitine in sports supplements. There are several forms of release:
- In liquid form. This is actually a ready-made carnitine with the fastest action - guarantees an energy boost 15 minutes before training. It is expensive, has high bioavailability and low efficacy.
- Powder. The best option for athletes, as it allows you to independently adjust the dosage of the amino acid. The only condition is that carnitine should be taken 40 minutes before training.
- Available as capsules and tablets. Useless and unnecessary drug that is sold in pharmacies. Low potency, low bioavailability, zero effect.
- As a component for an energy drink. Carnitine as a component increases the transfer functions of cells, which stabilizes and prolongs the effects of energy.
- As a pre-workout component.
Table of foods containing l-carnitine
If you decide to consume L-carnitine exclusively from natural products, you will need a table that shows which foods contain carnitine.
| Product (100 g) | The amount of carnitine in mg |
| Avocado (1 pc.) | 2 |
| White bread | 0.1 |
| Beef | 85 |
| Chicken breast | 3–5 |
| Pasta | 0.1 |
| Milk | 3-4 |
| Ice cream | 3-4 |
| Rice | 0.04 |
| Pork | 27 |
| Asparagus, ready | 0.2 |
| Cheese | 2-4 |
| Cottage cheese | 1 |
| Cod | 4–7 |
| Whole wheat bread | 0.2 |
| Eggs | 0.01 |
Potential harm
Doctors constantly tell the population about the risk of consuming excessive amounts of red meat. High levels of saturated fat and cholesterol are known to damage the heart. However, new research has shown that in addition to cholesterol, L-carnitine also has harmful effects.
Taking carnitine is believed to increase energy, accelerate weight loss, and improve athletic performance. For this reason, some energy drinks contain L-carnitine. However, the mechanism of this phenomenon is not as simple as it seems.
Here's how it works: After you ingest L-carnitine, it travels to the intestines, and intestinal bacteria convert the L-carnitine into a substance called TMA, which is then processed by the liver. The liver converts TMA into a compound that has been linked to plaque formation in arteries and heart disease. This transformation is most intense in those who regularly consume red meat. Notably, vegans and vegetarians, even after consuming large amounts of carnitine, do not get significant levels of TMA. This is likely because they have different gut bacteria.
Red meat is one of the most abundant sources of L-carnitine at around 56-162 mg per serving. L-carnitine can also be found in foods like pork, seafood, and chicken, but at much lower levels - 3 to 7 mg per serving. Dairy products such as ice cream, milk, and cheese range from 3 to 8 mg per serving. However, supplements are the main source of L-carnitine for many people - some take up to 500-1000 mg per day. The more L-Carnitine you get, the more TMA you risk getting, which can damage your blood vessels even faster.
What follows from this. It's very simple - taking carnitine in combination with a large amount of fatty acids leads to the accumulation of bad cholesterol and the appearance of cholesterol plaques.
Doctors give preventive recommendations:
- Do not consume polyunsaturated omega 6 fats on the same days as carnitine.
- Avoid foods high in natural carnitine, protein and cholesterol.
- Do not take L-Carnitine outside of your workout routine.
Despite all the benefits of carnitine, the enhancement of its transport properties in the composition of protein - the main vehicle for harmful cholesterol - completely negates all the useful properties of the substance.
© apichsn - stock.adobe.com
Difference between l and D
Editors Note - This section is presented for the most curious. Finding D-carnitine supplements is nearly impossible. At the same time, artificially limiting its synthesis also does not seem realistic.
D-carnitine acts as an antagonist of L-carnitine as an agent that reduces the production of lactic acid. The amino acid is similar in composition to L-carnitine, except for a few branched chains.
Its main purpose:
- increased catabolism;
- slowing down the transport of fatty acids to mitochondria;
- increased accumulation of lactic acid.
Do you think this is unpleasant and harmful to the body? You are only half right. Lactic acid, which accumulates in the muscles, stimulates the process of building new tissues. And slowing down the transport of fatty acids is necessary to regulate metabolism while reducing physical activity. Strengthening catabolism with open insulin cells eliminates excess mass and toxins in the body. Taken together, all carnitine not spent in a day can be freely transformed into D-carnitine, and vice versa.

© pictoores - stock.adobe.com
Recent Research
Carnitine is not yet fully understood by modern medicine. Until now, disputes regarding its harm and benefits do not subside. In addition, the Olympic Committee is going to decide on the inclusion of artificial carnitine in the list of prohibited substances. At the same time, recent studies by the American portal Nature medicine have made several discoveries regarding the potential harm that the intake of this substance can have.
It is important for us to understand the basic principles of a moderate diet. Even substances synthesized by the body can be harmful. Studies show that carnitine overdose can rarely cause:
- water intoxication;
- hyponatremia;
- recoil effect on the strength of heart contractions.
Outcome
Athletes can safely consume l-carnitine in the form of an additional stimulant during drying and to preserve the heart. If you are consuming additional L-carnitine, we recommend not exceeding 2000 mg (2 g) per day. Non-athletic people who regularly consume meat do not need to purchase additional carnitine.
When it comes to using the product for CrossFit athletes, carnitine will initially reduce the risk of rhabdomyliosis. In the future, with full adaptation of the body to stress, the use of carnitine will not significantly affect the athlete's performance. There are no specific contraindications to the use of this remedy. It is actively promoted in pharmacies for women, and in sports clubs for men.








