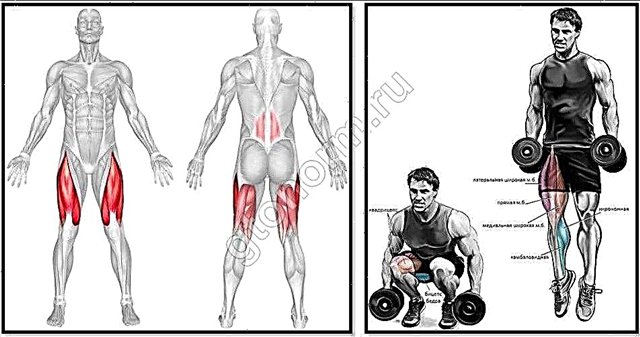
The hydrolyzed form of collagen, gelatin, is of great importance for the joints. It is a structural protein found in every tissue in the body. It accounts for about 6% of the total body weight. Collagen saturated with calcium compounds forms the basis of human bones. Cartilage and tendons are similarly arranged. Only the percentage of calcination in them is less. They lose protein and calcium as they age, causing osteoporosis. Such changes are especially undesirable for athletes. Therefore, it is important to make up for these losses. It seems that the way out is gelatin.
Myths and facts
Hydrolyzed collagen is obtained by heat treatment of animal collagen fibers and is completely analogous to anthropogenic one. It is usually used in the food industry under the name of gelatin. As for sports, it has only recently begun to find widespread use there. Until now, unscrupulous manufacturers of dietary supplements neglected them because of its cheapness and offered athletes expensive collagen courses, appealing that the amino acid composition of the substance is unsuitable for the construction of new high-grade protein molecules.
In fact this is not true. Despite the fact that gelatin partially loses collagen amino acids during heat treatment, it is able to make joints and ligaments stronger. It includes:
- Proteins and amino acids.
- Fatty acid.
- Polysaccharides.
- Iron.
- Minerals.
- Vitamin PP.
- Starch, ash, water - in small quantities.
Being, in fact, a hydrolyzed protein, it perfectly restores ligaments. They began to use this property for the rehabilitation of muscles, increasing their mass, but all in vain. The effect of hydrolyzed collagen was limited to the joint surfaces. The explanation is simple: the articular tissues demineralized by age, like a sponge, absorb the substance that comes with food.

As a result:
- The site of injury or fracture is being restored.
- Bone and cartilaginous calluses form faster.
- Hair begins to grow.
But muscles have a different composition, and hydrolyzed collagen has practically no effect on them. It does not stop inflammation, autoimmune shifts, so serious diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, for example, are not treated. To remineralize bones and ligaments, you need at least 80 g of pure gelatin daily. This is problematic, therefore, it is usually taken for a long time in order to achieve the intended effect.
Hydrolyzed collagen is unable to relieve pain. And this is also his minus, if we talk about medicinal properties. But it stimulates regeneration, and the rehabilitated tissues are inert to inflammatory processes and do not hurt. Therefore, as the joint recovers, the inflammation stops on its own. Hence the conclusion: with regular, long-term and correctly dosed intake - gelatin, as an adjuvant in therapy, is quite justified.
The use of gelatin in sports
Hydrolyzed collagen is absorbed from the digestive tract in the form of oligopeptides - chains of amino acids. Entering the blood, it is delivered with its current to the place that needs regeneration. The essence of the action is the ability to restore cartilage, ligaments, tendons by increasing the density of collagen fibers and the number of fibroblasts, which stimulate the synthesis of their own connective tissue fibers.
Taking gelatin at a dose of 5 g per day for a week allows you to visually improve the condition of all tissues, which are based on protein fiber: skin, joints, mucous membranes. Practically start their resuscitation. And all this is not when taking expensive collagen courses, but only on the basis of edible gelatin, which is quite inexpensive.
As for the muscles, they get an improvement in blood supply due to the presence of 8% arginine in gelatin. And already on this basis, with the help of training according to a special program, a real increase in muscle mass is achieved. In bodybuilding, it is very important to have strong joints and ligaments, so the benefits of gelatin are unambiguous. And at that age when the synthesis of its own collagen tends to zero, this is doubly important. Older athletes usually take gelatin in combination with vitamin C to prevent tendon sprains and joint injuries.
The regenerative capacity of collagen affects the entire joint and the muscle fibers that go to it. As a result, rehabilitation after training or competition is faster and more efficient, cell division is stimulated. The effect of gelatin is not inferior in its effectiveness to the collagen complex.
Properties and indications for use
Both in medical practice and in sports, gelatin is prescribed if:
- There is a crunch and aches in the joints, especially at night, discomfort when walking.
- The pain is accompanied by swelling over the area of damage.
- Pathological changes in the musculoskeletal system were revealed.
- Joint mobility is limited, stiffness appears.
- Erythema, swelling of the supra-articular surface is visualized.
- A diagnosis of arthrosis or arthritis is made.
In cases of minor discomfort and crunching, the effect occurs within a couple of weeks:
- Cartilage regenerates.
- Ligaments are being restored.
- Demineralization is inhibited.
- The growth of hair shafts is activated, the condition of the nail plates is improved.
- Metabolism, brain activity and memory are improved.
The qualities of gelatin are similar to those of collagen. It perfectly restores joint tissues, heals the body as a whole. In addition, it is rapidly absorbed in the intestine, which is important for the severity of the pathological process.
Contraindications
Hydrolyzed collagen has few limitations to its use:
- High blood clotting.
- Vascular pathology.
- ZhKB and MKB.
- Problems with the digestive system.
- Hemorrhoids.
- Individual intolerance.
- Sensitization with gelatin.
- Gout.
- CKD.
- Exchange violations.
For the prevention of intestinal problems, it is advised to combine the intake of gelatin with natural laxatives: prunes, beets, kefir, dried apricots. Senna is also useful.
Recipe: 200 g of natural laxatives are mixed with 50 g of herbs, brewed with a liter of boiling water and infused. Drink chilled in a teaspoon at night. Store in a glass container in the refrigerator. The product can be frozen if placed in a plastic container.
Terms of use
Gelatin is not a panacea for joint diseases. It is effective in the early stages of pathology and for its prevention. In this case, the substance should be taken daily, 5-10 g in the form of a powder or granules.
They are added to any liquid or taken dry. The methods of making medicinal cocktails are different. The most popular is gelatin on water: in the evening, several small spoons of the substance are poured with half a glass of ordinary water at room temperature. In the morning, the resulting mass is diluted with another half glass of water, but already warm and drunk on an empty stomach for 20 minutes before eating. The course is 14 days. Can be sweetened with honey. If drinking is difficult, it is recommended to make a fresh drink every three days.
Dry gelatin is commonly used by patients or athletes who are monitoring their weight. It is added by 5 g to any dietary product. The only condition is the absence of intestinal problems. Eat in small portions throughout the day. Compresses on joints or applications are made of gelatin, which reduces swelling and inflammation.
In power sports, gelatin is consumed twice a day, 5 g after meals. It is safe and easy to combine with other drugs. The reception methods are as follows:
- The powder is washed down with a large amount of your favorite liquid: water, juice.
- Pre-mixed in water and drunk immediately.
- Jelly is being prepared.
- Add to gainer or protein.
The best recipes
We offer time and results-tested ways of using gelatin:
- With milk: dissolve 3 small tablespoons of gelatin in 2/3 cup of warm milk. After half an hour, the resulting lumps are stirred, and the mass is heated in the microwave until they are completely dissolved. Add a little honey or sugar, cool and refrigerate. Jelly is eaten in a spoon three times a day for a week. In this case, calcium from milk also works, strengthening the tissues.
- Aqueous solutions of gelatin can be used warm with a spoonful of honey - this is a guarantee of tissue nutrition with the necessary microelements and biologically active substances. Honey only tolerates warm water, in any other it loses its beneficial properties. Therefore, doctors forbid boiling it.
- Compress. A bag of gelatin is distributed between layers of cheesecloth folded in four and pre-soaked in moisture. This design wraps the joint, on top - cellophane under a warm scarf or shawl for a couple of hours. Warmth should be felt. Frequency rate: twice a week. Course: month with a break of 30 days.
This use of gelatin is justified for both medicinal and sports purposes. It contributes to the full and effective strengthening of the cartilage and ligaments of the joint capsule, their reliable operation with additional physical exertion.

Dietary supplement with gelatin BioTech Hyaluronic Collagen
Preparations with gelatin
If athletes are guided by pharmacy gelatin or dietary supplements based on it, then each drug is accompanied by the corresponding instructions for use. However, few manufacturers use gelatin as an additive in medicinal creams, ointments, tablets, since it is easier to introduce synthetic analogs into the medicine. But there are still such:
- Women's formula from the American company Farmamed. The tablet contains 25 g of gelatin, vitamins of all groups, minerals, metal ions. Take a piece three times a day with meals. Course - month. Since the drug is a multivitamin complex, it removes toxins and free radicals from the body.
- Capsule gelatin from the 21st century company. Available in 100 pieces, taken in a capsule with food, three times a day, up to three months.
- BioTech Hyaluronic & Collagen is a sports dietary supplement that supports joints and all elements of the intra-articular bag in proper condition. It is taken once a day, 2 capsules with meals.