Vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin. The ordinary people know very little about its use and benefits, it is not as common in supplements as, for example, vitamins A, E or C. This is due to the fact that a sufficient amount of phylloquinone is synthesized in a normally functioning body, vitamin deficiency occurs only in certain diseases or individual characteristics (lifestyle, workload, professional activity).
In an alkaline environment, phylloquinone decomposes, the same happens when exposed to direct sunlight.
In total, the group of vitamins K combines seven elements that are similar in molecular structure and properties. Their letter designation was also supplemented with numbers from 1 to 7, corresponding to the opening order. But only the first two vitamins, K1 and K2, are synthesized independently and are naturally occurring. All others are synthesized only under laboratory conditions.
Significance for the body
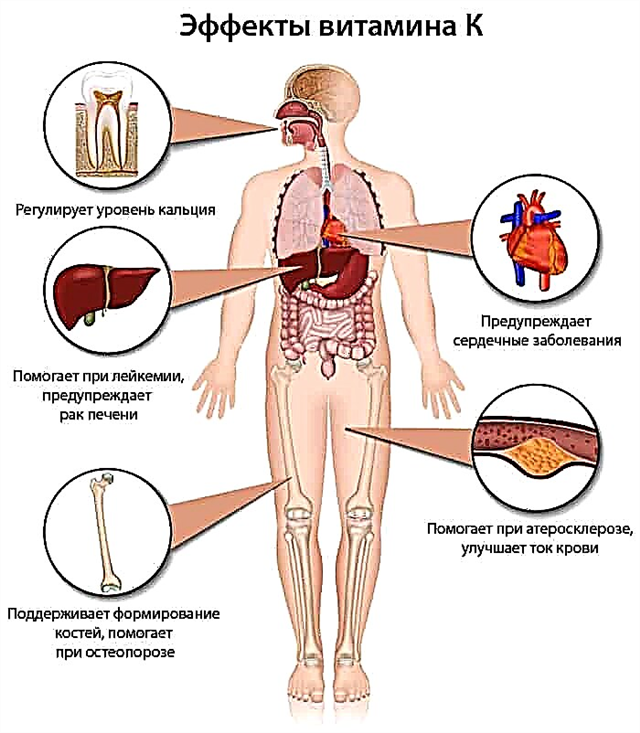
The main function of vitamin K in the body is to synthesize blood protein, which is essential for the blood clotting process. Without a sufficient amount of phylloquinone, the blood does not thicken, which leads to its large losses during injuries. Vitamin also regulates the concentration of platelets in plasma, which are able to "patch" the site of vascular damage.
Phylloquinone is involved in the formation of transport proteins, thanks to which nutrients and oxygen are delivered to tissues and internal organs. This is especially important for cartilage and bone cells.
Vitamin K plays an important role in anaerobic respiration. Its essence lies in the oxidation of substrates without the participation of oxygen consumed by the respiratory system. That is, oxygenation of cells occurs due to the internal resources of the body. Such a process is necessary for professional athletes and all those who regularly attend training due to increased oxygen consumption.
© bilderzwerg - stock.adobe.com
In young children and the elderly, the synthesis of vitamins does not always take place in sufficient volume, therefore, often, it is they who experience vitamin deficiency to a greater extent. With a deficiency of vitamin K, there is a risk of osteoporosis (decreased bone density and increased fragility), hypoxia.
Phylloquinone properties:
- Accelerates the recovery process from injuries.
- Prevents internal bleeding.
- Participates in the oxidation process when there is a lack of external oxygen.
- Supports healthy cartilage and joints.
- It is a means of preventing osteoporosis.
- Helps to reduce the manifestation of toxicosis in pregnant women.
- Fights liver and kidney diseases.
© rosinka79 - stock.adobe.com
Instructions for use (norm)
The dose of the vitamin, at which the normal functioning of the body will be maintained, depends on the age, the presence of concomitant diseases, and the physical activity of the person.
Scientists have derived the average value of the daily requirement for phylloquinone. This figure is 0.5 mg for a healthy adult who does not subject the body to intense exertion. Below are the indicators of the norm for different ages.
| Contingent | Normal indicator, μg |
| Infants and children under three months | 2 |
| Children from 3 to 12 months | 2,5 |
| Children from 1 to 3 years old | 20-30 |
| Children from 4 to 8 years old | 30-55 |
| Children from 8 to 14 years old | 40-60 |
| Children from 14 to 18 years old | 50-75 |
| Adults from 18 years old | 90-120 |
| Lactating women | 140 |
| Pregnant | 80-120 |
Content in products
Vitamin K is found in greater concentration in plant foods.
| Name | 100 g of product contains | % of the daily value |
| Parsley | 1640 μg | 1367% |
| Spinach | 483 μg | 403% |
| Basil | 415 μg | 346% |
| Cilantro (greens) | 310 mcg | 258% |
| Lettuce leaves | 173 mcg | 144% |
| Green onion feathers | 167 mcg | 139% |
| Broccoli | 102 μg | 85% |
| White cabbage | 76 μg | 63% |
| Prunes | 59.5 μg | 50% |
| Pine nuts | 53.9 μg | 45% |
| Chinese cabbage | 42.9 μg | 36% |
| Celery root | 41 μg | 34% |
| Kiwi | 40.3 μg | 34% |
| Cashew nuts | 34.1 μg | 28% |
| Avocado | 21 μg | 18% |
| Blackberry | 19.8 μg | 17% |
| Pomegranate seeds | 16.4 μg | 14% |
| Fresh cucumber | 16.4 μg | 14% |
| Grapes | 14.6 μg | 12% |
| Hazelnut | 14.2 μg | 12% |
| Carrot | 13.2 μg | 11% |
It should be noted that heat treatment often not only does not destroy the vitamin, but, on the contrary, enhances its effect. But freezing reduces the effectiveness of the reception by about a third.

© elenabsl - stock.adobe.com
Vitamin K deficiency
Vitamin K is synthesized in sufficient quantities in a healthy body, therefore its deficiency is quite rare, and the symptoms of its deficiency are expressed in the deterioration of blood clotting. Initially, the production of prothrombin decreases, which is responsible for the thickening of blood when it flows out of the wound in open areas of the skin. Later, internal bleeding begins, hemorrhagic syndrome develops. Further vitamin deficiency leads to ulceration, blood loss and kidney failure. Hypovitaminosis can also cause osteoporosis, cartilage ossification and bone destruction.
There are a number of chronic diseases in which the amount of synthesized phylloquinone decreases:
- serious liver disease (cirrhosis, hepatitis);
- pancreatitis and tumors of various genesis of the pancreas;
- stones in the gallbladder;
- impaired motility of the biliary tract (dyskinesia).
Interaction with other substances
Due to the fact that natural synthesis of vitamin K occurs in the intestines, prolonged use of antibiotics and an imbalance of microflora can lead to a decrease in its amount.
Garlic and anticoagulant drugs have an overwhelming effect. They block the performance of the vitamin.
Reducing its amount and drugs used in chemotherapy, as well as sedatives.
Fatty components and fat-containing additives, on the contrary, improve the absorption of vitamin K, therefore it is recommended to take it together with fish oil or, for example, fatty fermented milk products.
Alcohol and preservatives decrease the rate of phylloquinone production and decrease its concentration.
Indications for admission
- internal bleeding;
- a stomach or duodenal ulcer;
- load on the musculoskeletal system;
- intestinal disorders;
- long-term antibiotic treatment;
- liver disease;
- long healing wounds;
- hemorrhages of various origins;
- osteoporosis;
- fragility of blood vessels;
- menopause.
Excess vitamin and contraindications
Cases of excess vitamin K practically do not occur in medical practice, but you should not take vitamin supplements uncontrollably and exceed the recommended dose. This can lead to thickening of the blood and the formation of blood clots in the vessels.
Reception of phylloquinone should be limited when:
- increased blood clotting;
- thrombosis;
- embolism;
- individual intolerance.
Vitamin K for athletes
People who exercise regularly need additional amounts of vitamin K, as it is consumed much more intensively.
This vitamin helps to strengthen bones, joints, increases the elasticity of cartilage tissue, and also accelerates the delivery of nutrients to the joint capsule.
Phylloquinone supplies cells with additional oxygen, which muscle tissue lacks during exhausting workouts.
In the case of sports injuries accompanied by bleeding, it regulates blood clotting and accelerates their healing.
Phylloquinone supplements
Name | Manufacturer | Release form | Price, rub | Packing photo |
| Vitamin K2 as MK-7 | Healthy origins | 100 mcg, 180 tablets | 1500 | |
| Super K with Advanced K2 Complex | Life Extension | 2600 mcg, 90 tablets | 1500 | |
| Vitamins D and K with Sea-Iodine | Life Extension | 2100 mcg, 60 capsules | 1200 | |
| MK-7 Vitamin K-2 | Now Foods | 100 mcg, 120 capsules | 1900 | |
| Natural Vitamin K2 MK-7 with Mena Q7 | Doctor's Best | 100 mcg, 60 capsules | 1200 | |
| Naturally Sourced Vitamin K2 | Solgar | 100 mcg, 50 tablets | 1000 |









