Violation of the physiological and anatomical connections of the spinal canal and the spine is called spinal cord injury. An imbalance of this kind entails a loss of mobility, in some cases with irreversible consequences.
Injury to the spine and spinal cord is the result of falls, accidents, collapsing buildings, beating or other aggressive actions.
People with a diagnosis of spinal cord injury or suspected of such injuries are brought to neurosurgery, or traumatology, depending on the severity of the case. If the injury is classified as relatively mild, the patient is placed for neurological treatment.
Classification of spinal cord injuries
In 1997, the Ministry of Health in Russia introduced a new classification system for diseases. A more accurate coding, including alphabetic and numeric parameters, made it possible to expand the list and clarify many factors of violations.
According to ICD-10, diseases of the spinal cord are classified under the letter S, the consequences of injuries - T.
The correct diagnosis allows you to prescribe the right treatment. In spinal cord injuries, the speed of decision-making and therapy prescription largely affects the patient's further ability to maintain motor functions. Therefore, at the initial stage, the functional state is not assessed, the severity of the damage is considered, and surgical or conservative treatment is prescribed.

© magicmine - stock.adobe.com
Damage is classified into 3 main types:
- Isolated.
- Combined - includes mechanical disorders of neighboring organs.
- Combined - complicated by radiation, toxic or other factors that aggravate the patient's condition.
There is also a classification of SCI according to the characteristics of violations:
- Closed - without damaging the soft paravertebral tissues.
- Open - without penetration into the spinal canal.
- Open penetrating wounds are of several types:
- Through - characterized by the fact that the object that has damaged the spine passes to the flight.
- Blind - due to the delay of the object in the spinal canal.
- The tangents affect the spine partially.
Open wounds related to categories 2 and 3 are subdivided into gunshot (shrapnel, bullet) and non-fire (chopped, cut, stabbed). The most dangerous to life are bullet.
Spinal cord injuries are classified into the following types:
- contusion (the consequences are determined 3 weeks after the elimination of spinal shock, leading to an imbalance of reflex activity);
- shake;
- hemorrhage or intracerebral hematoma;
- rupture of the capsular-ligamentous apparatus of the vertebral motor segment;
- dislocation of the vertebrae, can be of varying severity;
- disk rupture;
- fracture, as well as a fracture with displacement;
- compression (earlier, later, acute) with the subsequent development of compression myelopathy;
- injuries to the main vessel (traumatic heart attack);
- various injuries of the roots of the spinal nerves;
- complete spinal cord injuries are the most dangerous and irreversible.
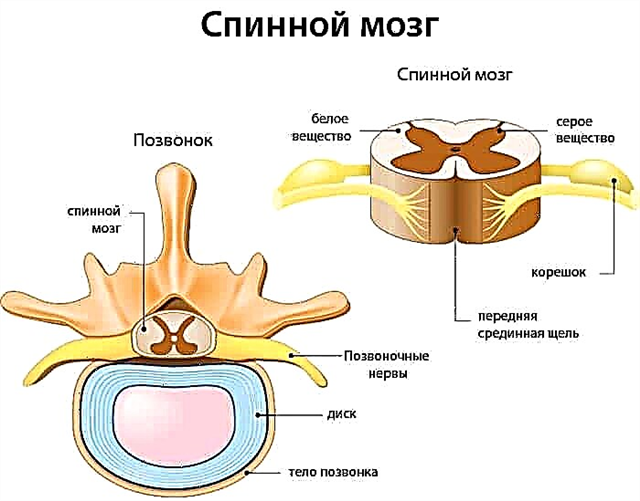
© designua - stock.adobe.com
The occurrence of disorders in several places of the spine is systematized as:
- Multiple - disorders in the nearby vertebrae or vertebral discs.
- Multilevel - damage to vertebrae or discs distant from each other.
- Multiple multi-level - combine the characteristics of the previous two types.
Symptoms in different cases
Spinal injury symptoms are slow onset and tend to change over time. This is due to the fact that there is a partial death of nerve cells in the acute period, later massive destruction can occur. They are provoked by the following factors: self-destruction of defective tissues, lack of nutritional components, poor oxygen saturation, intoxication.
The course of the disease is characterized by certain changes and is divided into periods:
- acute - 3 days after injury;
- early - no more than 30 days;
- intermediate - 90 days;
- late - 2-3 years after the accident;
- residual - the consequences after many years.
The first stages are characterized by symptoms with pronounced neurological manifestations: loss of sensitivity, paralysis. Later periods are expressed in organic changes: necrosis, degeneration.
The clinical picture depends on the site of injury and the severity of the disorder. The factors of occurrence of a particular injury are also taken into account. All this should be considered systematically.
All types of spinal injuries have their own symptoms, and in each spine they manifest themselves differently (cervical, thoracic and lumbar). We will consider this in the tables below.
Spinal cord root injuries
| Cervical | Pectoral | Lumbar |
| Pain in the upper back, from the lower edge of the shoulder blades and above. Feeling numb. Stiffness in upper limbs. | Pain in the back and ribs that gets worse when doing anything. Sharp severe pain radiating to the region of the heart. | Pain in the lumbar region, thighs and buttocks due to pinched sciatic nerve. Paresis of the legs and arms. Sexual dysfunction, impaired control of urination and defecation. |
Spinal cord bruises
| Cervical | Pectoral | Lumbar |
| Swelling of the damaged area. Loss of sensation in the neck, shoulders, and upper limbs. Impaired motility of the neck and arms. In severe cases, memory loss, visual and auditory dysfunction. | Swelling of the damaged area. Pain in the back and heart. Imbalance of the respiratory, digestive, and urinary systems. | Numbness of the area of injury. Pain in standing and sitting position. Dysfunction of the lower extremities. |
Concussions in the spine
Concussions in the spine are fraught with the following manifestations:
| Cervical | Pectoral | Lumbar |
| General weakness, paresis of the upper limbs. | Labored breathing. | Paresis of the lower extremities. Violation of urination. |
Almost all spinal injuries are associated with the fact that sensitivity immediately disappears at the site of injury. This condition persists, depending on the severity of the violations, from a couple of hours to several days.
Crushing
When squeezed, the symptoms will be the same regardless of the location of the injury:
- Partial loss of sensitivity.
- Pain.
- Burning effect.
- Weakness.
- Cramping.
- Motor dysfunction.
Contusion
In case of contusions, the patient feels a temporary loss of motor functions, reflex imbalance, muscle weakness, all signs manifest themselves quickly, already in the first hours.
Spine fractures
In case of fractures, the symptoms are as follows:
| Cervical | Chest |
| Pain:
|
Fractures are characterized by a total imbalance in the body's activity, sensitivity disappears, the possibilities of motor activity of the lower extremities decrease.
Dislocations
Dislocations are characterized by the following symptoms:
| Cervical | Pectoral | Lumbar |
|
|
|
Spinal cord rupture
A rare and complex pathology - spinal cord rupture, is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Acute pain at the site of injury, often unbearable.
- Loss of sensation and complete paralysis as irreversible phenomena in the area located below the rupture.
Spinal Injury Emergency Care
Suspicion of a spinal injury requires a prompt call for qualified help. It is strictly forbidden to take any action without a medical education. Any manipulation with the victim can be fatal.
In case of spinal injuries as a result of an accident, it is permissible to provide assistance within the framework of the following recommendations:
- In order to avoid increasing deformity, the patient is fixed. In case of neck injuries, a firm collar is carefully put on, it is also called the Philadelphia collar.
- For severe injuries causing difficulty in breathing, inhale humidified oxygen using an oxygen cylinder with a removable mask attachment. It can be purchased at a nearby pharmacy. If the possibility of spontaneous breathing is impaired, a special tube is inserted into the trachea and artificial ventilation of the lungs is carried out.
- If the patient loses blood as a result of trauma, an intravenous injection of Refortan 500 and crystalloids is performed. These manipulations will restore blood pressure.
- If the injury is accompanied by severe pain, an analgesic is injected.
Success in the treatment of spinal injuries largely depends on the speed of first aid. If the victim is found, he is taken to the hospital as soon as possible.

© TeraVector - stock.adobe.com
First aid for spinal shock
Spinal shock manifestations are the result of serious injury. In such a situation, the main assistance to the victim will be quick and competent transportation to the hospital.
Spinal shock can be identified by the following criteria:
- Changes in body temperature and sweating.
- Dysfunction of internal organs.
- Increased pressure.
- Arrhythmia.
Shock occurs as a result of disorders in the spinal cord and can lead to a number of dire consequences. The patient is fixed on a hard surface, laying him face up or down.
The choice of position directly depends on the condition in which the victim was found. When moving, they maintain the position of the body in which the person was in order to avoid further deformations and deterioration of the condition.
In case of difficulty breathing, ensure the patency of the pathways. Artificial ventilation is performed.
Periods of injury
Damages are subdivided into periods:
- The first 2-3 days the acute stage lasts. At this time, it is difficult to draw conclusions about the form of injury, since the signs of spinal shock are most pronounced.
- Two to three weeks after injury is the early period. It is characterized by impaired reflex activity and conduction. Towards the end of this stage, spinal shock weakens.
- The true picture of violations is demonstrated by the intermediate period. Its duration is several months. In the absence of damage to the second motor neuron in the lumbar and cervical thickenings, reflexes are restored, and muscle tone increases.
- The final period continues throughout life. Gradually, the body restores its natural functions, the neurological picture stabilizes.
The first time after treatment, rehabilitation measures, both medical and social, are important. Especially for the victims who received the disabled status.

© tatomm - stock.adobe.com
Diagnostic methods
Diagnostics begins with interviewing the victim or witnesses of the accident. Instrumental and apparatus methods of examination are combined with neurological. The doctor examines and palpates.
In the process of collecting data and making a diagnosis, the physician is interested in the time of the injury and the mechanics of the incident. It is important where the patient feels the loss of sensitivity and motor functions. During the examination, they find out at what movements the pain sensations increase or decrease.
If the victim was taken to the clinic, eyewitnesses must report whether the victim moved after being wounded.
Neurological disorders that appear immediately after injury indicate a spinal cord injury. If, in the absence of spinal shock, the patient develops neurological signs, one can assume early or late compression of the spinal cord and its roots by hematoma or damaged bone or cartilaginous structures that descended into the spinal canal.
Full or partial memory loss requires a brain examination. In such cases, diagnosis is relevant, including X-ray and palpation examination. Loss of sensitivity in certain areas significantly complicates the diagnosis, therefore, all available methods of instrumental research are used. Until now, radiography is considered the fastest and most correct method of diagnosis; CT and MRI are also prescribed.

© Kadmy - stock.adobe.com
As a result of an external primary examination, deformations of the body are revealed and possible places of injury are noted. Based on this, follow-up studies are prescribed. Hematomas and depressions in the thoracic region indicate possible rib fractures, lung ruptures and other injuries. Visible defects in the thoracolumbar region can be accompanied by injury to the kidneys, liver and spleen.
When examining spinal injuries, it is impossible to determine the pathological mobility of the vertebrae by palpation, such manipulations lead to additional damage to the vessels and internal organs.
Instrumental examinations are carried out in order to clarify the localization, nature and causes of compression, features of spinal injury.
Treatment
If a spinal injury is suspected, immobilization is performed first. If an injured person is found unconscious, at the scene of accidents or after beating, the spinal region is also immobilized before the examination and exclusion of spinal wounds.
There are situations in which urgent surgical intervention is indicated:
- a constant increase in neuralgic signs, if the injury is not accompanied by spinal shock;
- blockage of the channels through which the cerebrospinal fluid moves;
- for violations of the spinal canal by squeezing objects;
- hemorrhage in the spinal cord, aggravated by blockade of the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid;
- diagnosed with compression of the main vessel of the spinal cord;
- disorders of the motor segments of the spine with an unstable character, posing a danger of repeated or periodic compression of the spinal cord.
Operations are contraindicated in the following cases:
- shock state with unstable dynamics (hemorrhagic or traumatic);
- injuries with concomitant violation of internal organs;
- traumatic brain injury of high severity, suspected intracranial hematoma;
- concomitant diseases accompanied by anemia.
Surgical intervention for spinal cord compression is performed urgently. Irreversible physiological transformations occur within 8 hours after injury. Therefore, the patient immediately goes to the intensive care unit or intensive care unit, where all contraindications to surgery are quickly eliminated.
The rehabilitation period after a spinal cord injury is long. The victim comes under the control of doctors, neurologists, vertebrologists and rehabilitation therapists. It is believed that a combination of physical therapy and physical therapy is most effective during the recovery period.
Forecast
About 50% of people with spinal injuries die in the preoperative period, most of them do not even reach medical facilities. After surgery, the mortality rate decreases to 4-5%, but can increase to 75% depending on the complexity of the injuries, the quality of medical care and other related factors.
Full or partial recovery of patients with SCI occurs approximately in 10% of cases, taking into account that the injury was stab-cut. With gunshot wounds, a favorable outcome is possible in 3% of cases. Complications arising during hospital stay are not excluded.
Diagnostics at a high level, operations to stabilize the spine and eliminate compression factors reduce the risk of a negative outcome. Modern implantable systems help to raise the patient faster, eliminating the negative consequences of a long period of immobility.
Effects
Any injury to the spine is accompanied by paralysis. This occurs as a result of a disruption in the activity of nerve cells. The duration and reversibility of immobility depends on the severity of the injury and the quality of care.
You can talk about the consequences of injury after 8 weeks, sometimes less. Around this period, spinal shock smoothes out and a clear picture of damage is visible. Usually at this time the preliminary diagnosis is confirmed.
Irreversible consequences arise when the spinal cord is crushed, which leads to a complete anatomical break.
The consequences and complications of spinal cord injury are divided into:
- Infectious and inflammatory - occur at different periods, are associated with damage to the urinary and respiratory systems.
- Neurotrophic and vascular disorders - appear as a result of muscle and organ atrophy. During the early period, the risk of deep vein thrombosis is high.
- Dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
- Orthopedic disorders - scaliosis, kyphosis, instability of damaged areas of the spine.