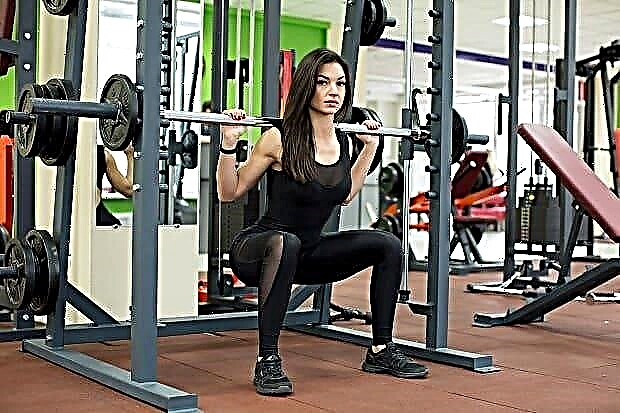
Squats with a barbell on the shoulders are a basic exercise common in CrossFit and powerlifting, involving a huge number of muscle groups. Along with the deadlift and bench press, it is a kind of indicator of the athlete's functional and strength training, and the correct technique for performing this exercise is critical. Today we will tell you how to do a squat with a barbell correctly, how to increase your results and how you can replace this exercise.
The barbell squat is an essential tool for developing muscle mass in the legs and buttocks, there is hardly at least one athlete in the world who does not perform squats, and at the same time boasts powerful quads. For this reason, this exercise has gained immense popularity in every gym in the world, and making progress in the squat is a significant goal for many experienced and not so athletes.
Today we will tell you about how to do barbell squats correctly - the exercise technique, as well as which muscles work, all the pros, cons and contraindications for heavy squats. And a lot of other useful information.
Why is this exercise needed?
Legs are our foundation, no matter what sport we do. Boxing, wrestling, crossfit, powerlifting, fitness - in none of these disciplines you will not achieve significant success if your legs do not receive sufficient load as part of your training process.
The barbell squat is perhaps the hardest exercise in existence. And not only physically, but also morally. Watch any powerlifting competition and notice how the lifters set themselves up before doing squatting attempts. It is unlikely that you want to get in the way of this person. Only in a state of insane courage can such superhuman weights be conquered.
With powerlifting sorted out, squatting is a competitive movement. What is the role of squats in CrossFit:
- Squats with a barbell on the shoulders are included in many complexes for athletes of different levels of training.
- Without a technically correct squat, you can forget about movements such as snatch, clean and jerk, thrusters, barbell lifting, etc.
- The squat is one of those exercises that inflates the intensity and pace of your workout. Performing really heavy squats requires frenzied energy, emotional mood and motivation, significantly increases the heart rate, which contributes to the lipolysis process.
What muscles work?
The main dynamic load falls on:
- Quadriceps;
- Hip biceps;
- Adductor muscles of the thigh;
- Gluteal muscles;
- Spine extensors.
The muscles of the press, gastrocnemius, soleus and trapezius muscles act as stabilizing muscles during the entire movement.

Pros and cons of barbell squats
The barbell squat is a basic, complex exercise that involves almost every major muscle group in your body. It is unlikely that at least one exercise, other than the deadlift, will be able to compare with the squat in this indicator. This kind of load cannot but lead to results: you become stronger, more enduring and more muscular.
The benefits of exercise
For men, heavy squats are exercise # 1. Numerous studies prove the hypothesis that performing this exercise leads to increased secretion of the main anabolic hormone - testosterone. It is this hormone that is responsible for all the traits inherent in a real man: physical strength and endurance, self-confidence, consistently high sexual energy, vigorous health, as well as what is commonly called "male charisma." For this reason, we recommend doing barbell squats for all men, regardless of age, unless there is a medical contraindication for this.
Start with small weights and gradually add discs to the bar, then over time you will see that not only have you made serious progress in your workouts in the gym, but in general you have become more confident and energetic.
However, all this does not mean that squats are a purely masculine exercise. For girls, squats with a bar should also become one of the foundations of the training process. It is this movement that puts the greatest strain on the hips and glutes and gives them an athletic shape.
In addition, doing squats intensively involves a fairly serious expenditure of energy. A few really hard sets will burn more calories than half an hour of walking on a treadmill. Therefore, squats should be performed not only if your goal is to pump up your legs and buttocks a little, but also during the period of getting rid of excess fat, so the drying process will proceed much more efficiently.
Potential harm from exercise
All the potential harm from barbell squats comes down to the consequences that are caused by a violation of technique. Severe deviations from the correct technique or working with critically heavy weights can lead to injuries of the knee ligaments and joints, as well as the occurrence of protrusions and hernias in the lumbar spine. Injuries to the shoulder joints and rotator cuff are also not uncommon. As a rule, they arise as a result of an incorrect (too low) position of the boom.
Barbell squats are also thought to have one unpleasant side effect - an increase in waist size. This is not entirely true, because your waist size is determined by genetics, the tendency of the obliques to hypertrophy and the volume of the stomach. However, the load on the obliques and abs during squats is really serious, and if you value your waist and feel that it starts to grow, then in squats and deadlifts it is better to slow down using a heavy weight. Squats also increase intra-abdominal pressure, which can lead to an umbilical hernia, but in most cases this problem can be avoided by using an athletic belt.
Contraindications
During squats with a barbell, a strong axial load is created on the spine, therefore this exercise is strictly contraindicated for all athletes who have any problems with the musculoskeletal system. The same goes for the knee or hip joints: if in the recent past you have had injuries, then doing squats with a barbell should be minimized. For the rehabilitation and recovery of injured tissue, it is better to use isolated exercises, such as flexion and extension of the legs in the machine.
Execution technique

There are many hypotheses regarding the correct squat technique with a barbell on the shoulders. Their number is due to the fact that the technique can vary due to the anatomical features of a particular person (for example, from the length of the limbs, the volume of the buttocks, flexibility in the hip and shoulder joints, etc.). Therefore, the recommendations listed below are of a purely general nature, a competent personal trainer can help you develop a more acceptable technique for you. Well, let's figure out how to do the right squat with a barbell.
Taking a barbell on your back
First phase of movement - remove the bar from the racks. Grasping the bar tightly at a width slightly wider than the shoulders, we squat under the bar exactly in the center of the bar, pressing into the bar with trapezoids, and remove the bar with the movement of our legs. It is extremely important to keep your back straight when removing the bar from the racks, since it is at this moment that our spine is experiencing maximum axial load.

Next phase - move away from the racks and fix. It is necessary to take a few steps with your back forward, find a stable stable position and start performing the exercise. Take your time when walking with your back forward, the movements should be smooth and confident. Otherwise, you will lose balance and control of movement, thereby risking injury.
Squat
Now you need to correctly perform the squat itself. There is no unequivocal opinion regarding such issues as: amplitude depth, leg width, body tilt level and degree of foot turn. It all depends on what goals you are pursuing.
- For example, if you are a performing powerlifter, a wider stance and a larger body tilt angle will suit you as this will allow you to lift more weight.
- If you want to work on the quadriceps in isolation, you should perform squats with parallel stance of the feet and in a shorter amplitude, for the buttocks, we perform a deep squat with a barbell.
The main thing - do not forget to keep your back straight and try not to pull your knees beyond the line of socks. at the lowest point of the amplitude, since this option for performing squats is monstrously traumatic. Remember breathing: exhalation is always done with effort.
Use an athletic belt while lifting heavy weights to keep your lower back in position and minimize the risk of an umbilical hernia. Another useful tip for strength athletes is that using weightlifting shoes instead of regular sneakers helps to somewhat reduce the range of motion. The last phase is to put the barbell on the racks. Keeping your balance and your back straight, take a few steps towards the racks and place carefully. Nothing complicated.
This video describes in detail the technique for performing the exercise, as well as the most common mistakes of crossfit beginners:
How to Increase the Barbell Squat?
Every second visitor to the gym wonders how to increase the squat with a barbell. There are many methods, but the meaning always lies in two aspects: competent cycling of loads (using percentages and alternating light / heavy workouts) and performing auxiliary exercises. In practice, a powerlifter preparing for a competition usually does two squat workouts per week, one of which works with a weight equal to 50-60% of maximum, 5 reps in three sets, and the other with a weight equal to 75-85% of maximum, 5 repetitions in five approaches. Closer to the competition, the weight of the bar increases, and the number of repetitions decreases.
For ancillary exercises, the preference is for the pause squat, front squat, barbell bend, bench squat, and overhead squat.
- Pause squats - a type of squat in which the athlete works in the deepest possible amplitude, fixing himself for a few seconds at the lowest point. The upward movement is explosive, thereby significantly increasing the speed of lifting with regular squats.
- Front squats differ from the classic squat with a barbell position of the bar - here it is on the chest. Thanks to this, the vector of movement changes slightly, and the quadriceps receives a more serious load.
- Barbell bends are extremely important for strength athletes, as they help to hold the body more stable during heavy squats.
- Bench squats - a kind of squats in a shorter amplitude (we go down above parallel), where our task is to go down to the bench level.
- Overhead Squat - coordination exercise, very difficult for beginners. Helps to better feel corners and blind spots.
Typical mistakes
If doing squats is not getting the results you want, then you are doing something wrong. Below is a short list of the most common mistakes that most novice athletes make:
Incorrect range of motion
Only deep squats have a really serious effect. If you do not even go down to the level of parallel with the floor, then do not expect results. At the lowest point, the back of the thigh should touch the calf muscles. Not all athletes do this right away due to weak stretching, so do not forget to stretch after training, special attention should be paid to the quadriceps and adductors of the thigh.

Rounding the back while lifting
This can be seen in every gym when an athlete squats with maximum weight. If your back is not strong enough to stay straight during heavy squats, then the weight should be reduced a little and you should start additional training of the spinal extensors. For this, hyperextensions with additional weights are best suited. The use of an athletic belt also partially solves this problem.

Movement in the lumbosacral spine
You may have seen more than once how some athletes "peck" with their coccyx at the lowest point of the amplitude. This makes lifting a little easier, but in no case should this be done - this is a direct path to injury.

Knee movement
Throughout the exercise, the knees should be in the same plane as the feet. Moving the knees inward relative to the proper trajectory is unacceptable. A meniscus injury can put an end to your sports career.

Incorrect feet position
Feet should be slightly unfolded and slightly wider than shoulder level. This is the only way you will be able to sit deeply enough without creating a strong load on the knee joint.

Incorrect breathing technique
Remember one simple rule: exhalation is always done with effort. Therefore, you need to inhale while going down, exhale - while lifting. If you do not follow this technique, your muscles will not receive enough oxygen and the effectiveness of the exercise will be greatly reduced. Deterioration of health, headache, nausea and fainting as a result of insufficient cerebral blood supply and increased intracranial pressure are also possible.
An alternative to the barbell squat
For medical reasons or other reasons, some gym goers stubbornly ignore an exercise such as a squat. How to replace squats with a barbell?
- Smith Squats... In this embodiment, the feet are slightly extended forward, which reduces the load on the knee joints.

© Artem - stock.adobe.com
- Hack squats... If you are lucky enough to find a good hack machine, you can safely start doing squats in it without worrying about your spine - the axial load is minimal here.

© splitov27 - stock.adobe.com
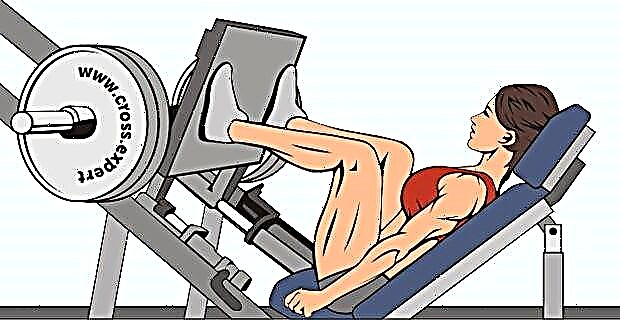
- Leg press... Biomechanically, this exercise is similar to the classic barbell squat, the work is carried out exclusively at the expense of flexion-extension of the knee joint, the quadriceps and adductor muscles of the thigh work more in isolation.
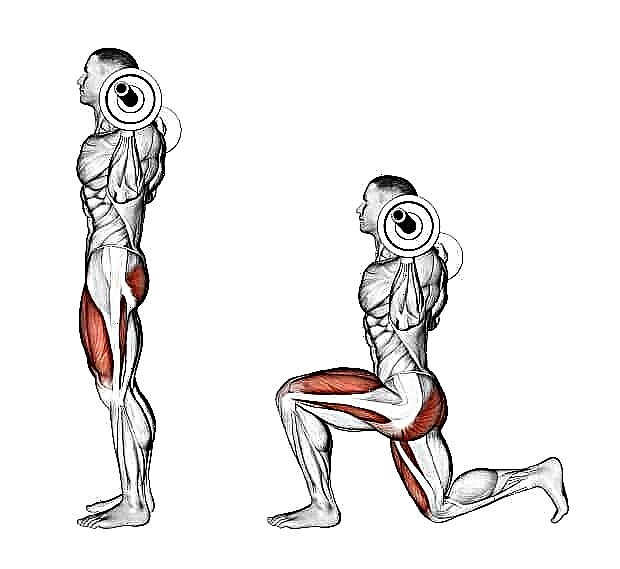
- Lunges... In lunges, there is an axial load on the spine, but the working weights are much less. The focus shifts to the adductors of the thigh and buttocks.
© Makatserchyk - stock.adobe.com
Perhaps these are 4 main exercises that can somehow compete with the squat in terms of the degree of stress assigned to the body. It's not only about the load on the muscles, but also about the general effect on the human body, in particular on its hormonal background - the fulfillment of heavy basic ones has a beneficial effect on the production of endogenous testosterone and growth hormone, which in turn will lead to an increase in strength indicators and muscle mass, increased libido and sexual activity, as well as the normalization of the reproductive system.
Standards for bare squat
Unfortunately, the federal budget of our country is not enough to promote the development of powerlifting, so we have only one federation officially accredited by the State Committee for Sports of the Russian Federation - the Russian Powerlifting Federation (RFP).
The standard is assigned by the sum of three movements (squats, bench press, deadlift). There is no separate set-up for squats. If you want to really test your strength, I highly recommend taking part in the competition. Competitions are regularly held throughout the Russian Federation, the calendar of competitions and regulations can be found on the official website of the federation.
There are also more than ten non-state federations operating on a commercial basis. The main funding comes from private investors, advertising of themed goods (sports nutrition, clothing and equipment) and entry fees for competition participants. The most popular non-state federation is the WPC / AWPC (no-doping / doping-controlled). Below are their bare-bones powerlifting guidelines for 2019.
Bit standards AWPC-Russia for powerlifting without equipment for men:
| Weight category | Elite | MSMK | MC | CCM | I rank | II category | III category | I jun. | II jun. |
| 52 | 490 | 432.5 | 377.5 | 340 | 302.5 | 265 | 227.5 | 187.5 | 150 |
| 56 | 532.5 | 470 | 410 | 367.5 | 327.5 | 287.5 | 245 | 205 | 162,5 |
| 60 | 570 | 505 | 440 | 395 | 350 | 307.5 | 262.5 | 220 | 175 |
| 67,5 | 635 | 562.5 | 490 | 440 | 392.5 | 342.5 | 292.5 | 245 | 195 |
| 75 | 692.5 | 612.5 | 532.5 | 480 | 425 | 372.5 | 320 | 265 | 212,5 |
| 82,5 | 737.5 | 652.5 | 567.5 | 510 | 455 | 397.5 | 340 | 285 | 227,5 |
| 90 | 777.5 | 687.5 | 597.5 | 537.5 | 477.5 | 417.5 | 357.5 | 297.5 | 240 |
| 100 | 817.5 | 725 | 630 | 567.5 | 502.5 | 440 | 377.5 | 315 | 252.5 |
| 110 | 852.5 | 752.5 | 655 | 590 | 525 | 457.5 | 392.5 | 327.5 | 262.5 |
| 125 | 890 | 787.5 | 685 | 617.5 | 547.5 | 480 | 410 | 342.5 | 275 |
| 140 | 920 | 812.5 | 707.5 | 635 | 565 | 495 | 425 | 352.5 | 282.5 |
| 140+ | 940 | 832.5 | 725 | 652.5 | 580 | 507.5 | 435 | 362.5 | 290 |
For women:
| Weight category | Elite | MSMK | MC | CCM | I rank | II category | III category | I jun. | II jun. |
| 44 | 287.5 | 255 | 222.5 | 200 | 177.5 | 155 | 132.5 | 110 | 90 |
| 48 | 317.5 | 282.5 | 245 | 220 | 195 | 172.5 | 147.5 | 122.5 | 97,5 |
| 52 | 345 | 305 | 265 | 240 | 212.5 | 185 | 160 | 132.5 | 107,5 |
| 56 | 372.5 | 327.5 | 285 | 257.5 | 227.5 | 200 | 172.5 | 142.5 | 115 |
| 60 | 395 | 350 | 302.5 | 272.5 | 242.5 | 212.5 | 182.5 | 152.5 | 122.5 |
| 67,5 | 432.5 | 382.5 | 332.5 | 300 | 265 | 232.5 | 200 | 165 | 132.5 |
| 75 | 462.5 | 410 | 355 | 320 | 285 | 250 | 212.5 | 177.5 | 142.5 |
| 82,5 | 487.5 | 432.5 | 375 | 337.5 | 300 | 262.5 | 225 | 187.5 | 150 |
| 90 | 507.5 | 450 | 390 | 352.5 | 312.5 | 272.5 | 235 | 195 | 157,5 |
| 90+ | 520 | 460 | 400 | 360 | 320 | 280 | 240 | 200 | 160 |
Crossfit squats with a barbell
Below are several complexes developed by adherents of functional training, which will help diversify your training process, as well as improve strength endurance, promote metabolism and use up the extra calories that you gain during the New Year holidays.
| Big deal | Do 800m running, 10 barbell squats, 800m running, 20 front squats, 800m running, 30 overhead squats. |
| Fight Gone Body | Perform the maximum number of burpees, pull-ups, push-ups, squats and sit-ups for the press, one minute for each exercise. There are 3 rounds in total. |
| Die hard | Perform 6 barbell squats, 8 tire bends, 12 pull-ups, 20 push-ups. Only 5 rounds. |
| Lunchbreak workout | Perform 10 standing barbell presses, 15 overhead squats, 20 barbell presses, 25 front squats, 30 barbell joggers, 35 classic barbell squats. |
| Fire in the hole | Perform 10 barbells to the chest, 10 barbell squats, 10 box jumps from deep sitting, and 8 push-ups on each arm. There are 3 rounds in total. |













