Knee ligament injuries are as common in CrossFit as they are in many other sports: weightlifting, athletics, powerlifting, football, hockey and many others. There may be many reasons for this, but most often three factors lead to this: improper exercise technique, huge working weight, and insufficient restoration of joints and ligaments between workouts.
Today we will look at how to avoid knee ligament injury while doing CrossFit, what exercises can contribute to this, and how to optimally recover from injuries.
Knee anatomy
Knee ligaments are responsible for the normal course of the main function of the knee joint - flexion, extension and rotation of the knee. Without these movements, normal movement of a person is impossible, not to mention fruitful sports.
The ligamentous apparatus of the knee has three groups of ligaments: lateral, posterior, intra-articular.
The lateral ligaments include the peroneal and tibial collateral ligaments. To the posterior ligaments - popliteal, arcuate, patellar ligament, medial and lateral supporting ligaments. Intra-articular ligaments are called cruciate (anterior and posterior) and transverse ligaments of the knee. Let us dwell a little more on the first ones, since every second athlete can face a cruciate ligament of the knee injury. The cruciate ligaments are responsible for stabilizing the knee joint, they keep the lower leg from shifting forward and backward. Recovery from a cruciate knee ligament injury is a long, painful and challenging process.
Also important elements in the knee structure are the outer and inner menisci. These are cartilage pads that act as a shock absorber in the joint and are responsible for stabilizing the position of the knee under load. Meniscus tear is one of the most common sports injuries.

© toricheks - stock.adobe.com
Injury Exercise
Below we present to your attention several of the most traumatic exercises used in sports, including in crossfit, which, if the technique is violated, can lead to damage to the knee ligaments.
Squats
This group can include all exercises where all or most of the amplitude is passed through squats, whether they are classic or front squats with a barbell, thrusters, barbell jerk and other exercises. Despite the fact that squats are the most anatomically comfortable exercise for the human body, a knee injury or ligament rupture during exercise is common. This most often occurs when the athlete is unable to handle the heavy weight when standing up and the knee joint "goes" slightly inward or outward relative to the normal trajectory of movement. This leads to injury to the lateral ligament of the knee.
Another cause of ligament injury while squatting is heavy working weight. Even if the technique is perfected, the heavy weight of weights puts a huge load on the knee ligaments, sooner or later this can lead to injury. For those athletes who do not use the principle of periodization of loads and do not allow their muscles, joints and ligaments to fully recover, this is observed everywhere. Preventive measures: use knee bandages, warm up thoroughly, recover better between hard workouts and pay more attention to the technique of performing the exercise.

© 6okean - stock.adobe.com
Jumping
All jumping exercises from CrossFit should be conventionally included in this group: squats with jumping out, jumping on a box, long and high jumps, etc. In these exercises, there are two points of amplitude where the knee joint is subject to heavy load: the moment of jumping up and the moment of landing.
The movement when jumping up is explosive, and, in addition to the quadriceps and gluteal muscles, the lion's share of the load falls on the knee joint. When landing, the situation is similar to squats - the knee can "go" forward or to the side. Sometimes, when performing jumping exercises, the athlete inadvertently lands on straight legs, in most cases this leads to injury to collateral or supporting ligaments. Preventive measures: do not land on straight legs, ensure the correct position of the knees when landing.

© alphaspirit - stock.adobe.com
Leg press and leg extension in the simulator
Of course, these are excellent exercises for the isolated study of the quadriceps muscle of the thigh, but if you think about their biomechanics, they absolutely contradict the angles that are natural for humans. And if in some leg press machines it is still possible to catch a comfortable amplitude and do a kind of "reverse squat", then sitting extension is the most uncomfortable exercise for our knees.
The simulator is designed in such a way that the main part of the load falls on the drop-shaped head of the quadriceps, which is simply impossible to load without creating a strong compression load on the knee joint. This problem is especially acute when working with large weights and a strong delay at the peak voltage point. Popliteal ligament injury becomes a matter of time. Therefore, we strongly recommend taking preventive measures: work with moderate weight, do not take long pauses at the top or bottom of the amplitude.
Remember, knee injury can often be prevented by controlling full range of motion and following correct exercise technique. Also, regular use of chondoprotectors will be a good preventive measure: chondroitin, glucosamine and collagen contained in them in large doses will make your ligaments stronger and more elastic. Also, athletes are advised to use warming ointments, this will not allow muscles, joints and ligaments to "cool down" between sets.

© Drobot Dean - stock.adobe.com

© Makatserchyk - stock.adobe.com
Types of knee ligament injuries
Traditionally, knee ligament injuries are considered an occupational disease in many athletes. However, even people far from sports can injure ligaments in an accident, strong blows to the shin, falls on the knee or jumping from great heights.
- A sprain is a knee injury that occurs due to overstretching of the ligaments, being subjected to too much stress. It is often accompanied by micro-tears of the ligaments.
- Ligament rupture - knee injury, accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the ligament fibers. Ligament rupture is of three degrees of severity:
- only a few fibers are damaged;
- more than half of the fibers are damaged, which limits the mobility of the knee joint;
- the ligament is torn completely or comes off from the place of fixation, the joint practically loses its mobility.
Symptoms of knee ligament injuries are the same: sharp severe pain in the knee, a cracking or clicking sensation under the kneecap, swelling, limitation of knee movement, inability to transfer body weight to the injured leg. To start the correct treatment of the knee after an injury (sprain or rupture of ligaments), you first need to make an accurate diagnosis, only a doctor can do this, you should not guess or diagnose "by eye" on your own, this can only be done with an X-ray, computed tomography , MRI or ultrasound.

© Aksana - stock.adobe.com
First aid
If your gym partner complains of severe knee pain, you or the instructor on duty should give them immediate first aid:
- Immediately apply cold to the injured area (wet towel, bottle of cold water, and best of all - an ice pack).
- Try to immobilize the knee joint as much as possible with an elastic bandage or improvised means (scarf, towels, etc.). The victim should not move a lot and in no case step on the injured leg.
- Give the injured leg an elevated position with the help of improvised means, the foot should be located above the level of the body, this will reduce the rate of edema formation.
- If the pain is extremely severe, give the victim pain medication.
- Immediately take the victim to the emergency room or wait for the ambulance to arrive.

© WavebreakmediaMicro - stock.adobe.com. Knee fixation
Treatment and rehabilitation after injury
In case of sprains or ruptures of the ligaments of the 1st severity, usually without surgery. It is necessary to limit the patient's movements to the maximum, use an elastic bandage or a special bandage, lift the injured leg above the level of the body, take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, use decongestant ointments.
In case of ruptures of the 3rd degree of severity or complete detachments of the ligament, it is already impossible to do without surgical intervention. An operation is performed to suture the ligaments, often using the fascia or tendons of the quadriceps to strengthen it. There are times when it is impossible to sew a ligament - the ends of the torn ligament are too far apart from each other. In this case, a prosthesis made of synthetic materials is used.
Rehabilitation after injury can be roughly divided into several stages:
- Physiotherapy (laser therapy, electrophoresis, ultraviolet radiation therapy);
- Exercise therapy (performing general strengthening exercises designed to restore the mobility and performance of the joint and ligaments).

© verve - stock.adobe.com. Laser physiotherapy
Exercises to restore ligaments
Now let's see how you can strengthen the knee ligaments after injury. Below is a small list of the simplest exercises for knee ligaments after injury, which at the initial stage should be performed under the supervision of a doctor or a rehabilitation therapist, and only after that - independently.
- Lying on your back, try to raise your straight legs up and lock in this position for a short time. Keep your legs as straight as possible.

© logo3in1 - stock.adobe.com
- Lying on your back, bend your knees, pull them to your stomach and freeze for a few seconds in this position. Return to starting position.

© comotomo - stock.adobe.com
- Using the support, try to stand on your heels and lift your toes up. At the same time, the legs at the knees should be straightened as much as you can.
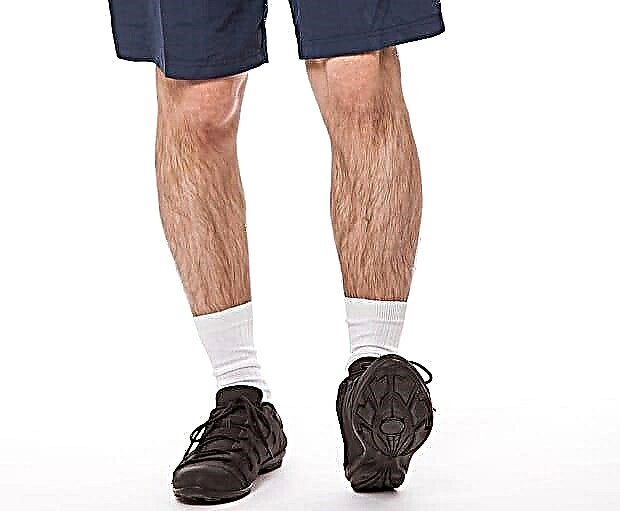
© smallblackcat - stock.adobe.com
- Using the support, try to stand on your toes and statically strain your calf muscles.

- Sitting on a chair and lifting your leg up, try to bend and straighten your knee as many times as possible.

© artinspiring - stock.adobe.com
- Try to perform the exercise "bicycle" smoothly and in a controlled manner.

© F8studio - stock.adobe.com
- Try to stretch your adductors and hamstrings in different positions: sitting, standing, or lying on your back.

© zsv3207 - stock.adobe.com
You should not include in your rehabilitation complex exercises that have a direct load on the quadriceps. It will strain not only the muscle, but also the knee joint, which in most cases will lead to severe pain and slow down the process of your recovery for a week or two.
















