Herniated disc of the lumbar spine - bulging of the intervertebral disc outside the vertebral bodies in the lumbar region. Locations: L3-L4, more often L4-L5 and L5-S1 (between the fifth lumbar and first sacral vertebrae). Diagnosed based on medical history, clinical symptoms, and CT or MRI data. In clinical practice, for convenience, bulging of more than 5-6 mm beyond the annulus fibrosus is usually called a hernia, less protrusion.
Hernia stages
The evolution of a hernia goes through a number of phases:
- Prolapse is a change under the influence of external factors in the physiological position of the disc, when eliminated, it is restored.
- Protrusion - the disc does not go beyond the conditional boundaries of the vertebral bodies, but strongly changes its position.
- Extrusion - the nucleus pulposus extends beyond the vertebral bodies.
- Sequestration - the release of the pulp outside.
If the hernial protrusion has migrated into the body of the superior or inferior vertebra, the pathological change is called Schmorl's hernia.

The appearance of the hernia on the model of the vertebrae. © rh2010 - stock.adobe.com
Causes and symptoms
Common causes of hernia include:
- Deterioration of trophism and development of degenerative changes in the area of the intervertebral disc, caused by:
- low physical activity;
- being overweight due to obesity;
- dysmetabolic processes (ankylosing spondylitis);
- infectious diseases (tuberculosis);
- incorrect distribution of the load on the spine due to:
- osteochondrosis;
- occupational hazards (constant driving);
- developmental anomalies of the spine or hip joint;
- acquired curvature (scoliosis);
- Excessive stress on the spine:
- lifting weights in an uncomfortable position;
- trauma.
The disease is manifested by lumbodynia, which in the debut is of a fickle nature and vertebral syndrome (asymmetric muscular-tonic changes that create favorable conditions for the development of scoliosis).
It can be complicated:
- Severe pain syndrome, poorly controlled by painkillers.
- Radiculopathy (radicular syndrome or lumboischialgia), accompanied by a complex of pathological changes in the legs:
- decrease or change in skin sensitivity (paresthesias);
- hypotrophy and muscle weakness.
- Myelopathy, characterized by:
- the extinction of tendon reflexes and the development of flaccid paresis on the legs;
- disturbances in the work of the pelvic organs (difficulty urinating and / or defecation, erectile dysfunction, extinction of libido, the appearance of frigidity).
The complications described above are indications for surgical treatment. The appearance of symptoms of discogenic myelopathy is the basis for resolving the issue of emergency surgery (the price is too high and the consequences can be catastrophic for health).
Which doctor treats
A neurologist (neuropathologist) treats hernia. Any clinician, suspecting this ailment, will without fail refer the patient to a neurologist for consultation, who, based on the clinical picture of the disease, the results of drug therapy and MRI data, can prescribe a neurosurgeon's consultation to decide on the expediency of surgical treatment.
MRI. © Olesia Bilkei - stock.adobe.com
Treatment methods
Hernia treatment can be conservative and operative. Depending on the chosen tactics, non-surgical treatment can be medication, physiotherapy, manual or surgical.
Manual therapy
Technique of manual "reduction" of discs. The average course duration is 10-15 procedures every 2 days.

© glisic_albina - stock.adobe.com
Drugs
The following medications are used for drug treatment:
- NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of ointments or tablets - Diclofenac, Movalis); the use of funds is aimed at relieving the symptoms of pain.
- central muscle relaxants (Midocalm, Sirdalud); the drugs promote soft relaxation of muscles experiencing increased irritation from the nerve cells involved in the pathological process.
- glucocorticoids (Diprospan, Dexamethasone); drugs stop inflammation, providing an indirect analgesic effect.
- paravertebral novocaine blockade, used to effectively relieve severe pain syndrome that is difficult to treat with NSAIDs;
- chondroprotectors and preparations with hyaluronic acid (Alflutop, Teraflex, Karipain, Rumalon); means have a trophic effect on cartilage tissue, enhancing its regeneration.
- B vitamins (contribute to the restoration of nervous tissue and nerve trunks).
Physiotherapy
This therapy includes:
- traction (reduces the load on the intervertebral discs);
- acupuncture (point reflexology); the technique is based on a reflex decrease in the severity of muscle-tonic syndrome;
- phonophoresis and electrophoresis (methods contribute to an increased flow of drugs into the affected area; the choice of funds remains with the attending physician);
- Exercise therapy (used to create a muscular corset from the autochthonous muscles of the back, designed to stabilize the spine and partially unload it);
- massage (to normalize muscle tone).

© DedMityay - stock.adobe.com
Operations
In cases where conservative treatment did not give the expected result, or the herniated disc has evolved and gave dangerous complications, surgical treatment is indicated, conditionally subdivided into:
- puncture laser valorization (provides for the removal of moisture from the deformed pulp to increase the strength of the intervertebral disc and prevent further increase in protrusion);
- electrothermal therapy (tasks similar to laser valorization);
- microdiscectomy (performed when the hernia size is less than 6 mm);
- discectomy (complete removal of the hernia);
- laminectomy (surgical expansion of the spinal canal; technologically complex surgery, characterized by a long recovery period);
- installation of B-Twin-implants (the operation is performed after discectomy to maintain the optimal intervertebral distance and stabilize the spine).
More often, at the conservative stage, specialists try to combine drug therapy and exercise therapy methods together with ERT. The complex of treatment is aimed at unloading the spine by strengthening the muscular corset and deep muscles of the back.
Difficulties can arise in women during pregnancy due to contraindications to the use of a number of medications and techniques.
Traditional medicine
They are based on a reflex effect on the affected areas during the period of remission.
They are used in the form of compresses prepared with 96% medical alcohol:
| Name of funds | Cooking method | Application method |
| Tincture of cinquefoil root | Dry roots are filled with ethanol. Withstand three weeks. | The tincture is applied orally in one teaspoon dissolved in 70 ml of water. |
| When added, Dimexidum is used topically for rubbing the legs and lower back. | ||
| Comfrey ointment | 500 g of fresh root is mixed with 500 g of melted pork fat, after which 300 ml of alcohol is poured. | Used as a compress. Apply to the affected area under a warm cloth for 30-40 minutes or overnight. |
| Compress with aloe and honey | Fresh aloe juice is mixed with honey and alcohol in a ratio of 1: 2: 3 and infused for 24 hours. | It is applied to gauze and applied to the affected area for an hour under a warm cloth. |
Exercise therapy methods
The duration of the workouts is from 10 minutes to half an hour. Designed for home use. The usual position is lying on your back. A roller should be placed under the lumbar region. The prone or lateral position is also used.
It should be remembered that when performing exercises, movements are performed smoothly, and gymnastics should bring a feeling of comfort.

© Jacob Lund - stock.adobe.com. Exercise with a roller under your back.
Gymnastic complex in the lying position:
- The arms are along the body. Inhalation and exhalation are performed. When inhaling, the arms and feet stretch towards themselves, when exhaling, the arms return to their original position, the legs relax.

- The same starting position. The head turns left and right, lingering in the center. At a count of times the head turns to the left, at a count of two in the center, at a count of three to the right, at a count of four again in the center.
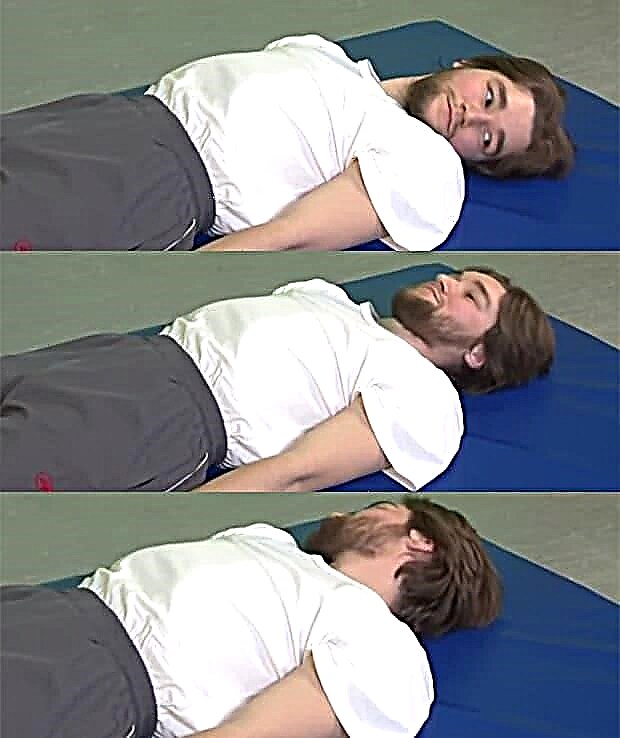

- The head is bent towards the chest, the socks towards oneself, on the count of two the head is on the mat, the legs relax.

- Hands are clenched into fists, legs slightly apart. Circular movements are performed with hands and feet 4 times outward and inward.

- Hands on your shoulders. Circular movements in the shoulder joints, 4 forward and backward.

- The right leg is bent at the knee and on the count of 2 is laid to the side, on the count of 3 it is bent again at the knee, on the count of 4 the starting position. The same is repeated with the left leg.

- The right arm and left leg are simultaneously retracted to the side. The same is repeated with other limbs.

- The foot stretches towards itself, trying to stretch the back of the leg.

- Hands along the body, legs bent at the knee joints. The abdominal muscles are tense.

- Hands behind the head, legs straight. The torso rises, the legs do not come off the floor.

In rehabilitology, treatment schemes for doctors have become widespread: Sergei Bubnovsky and Valentin Dikul.
V. Dikul's technique
Valentin Dikul's technique is based on dynamic stretching of the spine and symmetrical strengthening of the back muscles according to an individual program on special rehabilitation equipment designed to form your own muscle corset with an emphasis on problem areas. The consequence of the technique is the correction of scoliosis, kyphosis, kyphoscoliosis of varying severity.
Exercise with an elastic bandage according to a more simplified scheme can be performed at home, here we will consider some of the possible. Starting position standing.
- Perform bends with a straight back. The legs are slightly wider than the shoulders, the bandage is under the feet, and its ends are in the hands behind the head, the arms are bent, the elbows are to the sides. It is good to tilt the body, while leaving the legs straight, the bandage is pulled. Return to starting position.

- Next exercise: Raise your arms over the sides. Feet this time shoulder-width apart, bandage under the feet, and its ends in the hands. Simultaneously raise straight arms up through the sides to shoulder level.

- And the last exercise: mixing hands. The legs are again shoulder-width apart, the arms are slightly bent at the elbows, the bandage passes through the upper arms and lies on the shoulder blades. Bring your hands in front of your chest and return to the starting position.

All exercises are performed 10 to 20 times, depending on the condition, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
Complex of exercises by S. Bubnovsky
| Exercise name | Home position description | Execution method |
| Birch tree | Lying on his back with his arms raised up, the doctor fixes his legs with a cable to the MTB simulator. | The patient raises the pelvis with legs to their perpendicular position to the head. |
| Leg rotation | Lying on your side, holding on to the stand of the simulator with your hands. | The patient performs traction with a straight leg (lifting the working leg, while the leg does not bend) at the maximum amplitude. Returns to its original position. Performs 2-3 pulls for each leg if possible. |
| Frog | Lying on your stomach, arms extended forward. The doctor fixes a simulator of a certain weight on one of the legs. | The patient bends the leg, imitating the movements of an amphibian. |

Exercise birch

Leg Rotation Technique

Technique for the exercise "Frog"
Sports with a hernia of the lumbar spine
With a diagnosed intervertebral hernia, the following should be avoided:
- axial loads on the spine;
- shock loads (step aerobics, jumping);
- doing weightlifting.
Exercises for a herniated disc of the lumbar spine are useful:
- swimming (in remission, better - a crawl);
- Pilates exercise system (about 500);
- therapeutic fitness training;
- exercises on fitball;
- pull-ups on the horizontal bar (for men).
Prevention
Based on:
- Control over body weight in order to reduce the load on the intervertebral discs, especially in the lumbosacral and lumbar regions.
- Exclusion of hypodynamia, hypothermia of the lower back and prolonged static loads (work in a seated position - here in detail about the danger of a sedentary lifestyle).
- Use of special orthopedic mattresses.
- Wearing orthopedic braces and corsets that relieve the lumbar region.
- Exercise therapy. The set of exercises is aimed at strengthening the muscles of the back and is selected individually by the instructor.
- Healing walking. You should go smoothly rolling from heel to toe.
- Avoiding sudden stress on the spine; movements should be as smooth as possible.
- Eating food rich in B vitamins and cartilage derivatives.