Lumbar fracture - violation of the integrity of the vertebra (s). The pathogenesis is a strong unnatural bend when falling, hitting on the bent back. The pathological condition causes intense pain syndrome, stiffness of movements, muscle tension and swelling at the site of the lesion. Disorders in the functioning of the pelvic organs, paralysis, paresis can be observed. To make a diagnosis, use modern diagnostic methods of examination. In the absence of complications, a conservative therapy regimen is selected. In severe cases, surgical intervention is necessary.
The reasons
The pathological condition usually occurs when:
- Landing on your back.
- Diving into the water in shallow water.
- Sharp flexion or extension. This usually occurs when unexpected braking or when hitting a solid obstacle, the car in which the victim is.
- A blow to the lower back. Also, this type of injury is received by people involved in strength or active sports.

© rob3000 - stock.adobe.com
Development
Fractures are usually divided into:
- compression;
- dislocation fractures;
- fragmented.
The first type provokes:
- compression of the anterior region of the vertebra;
- its fragmentation;
- wedge-shaped flattening.
There are three degrees of compression:
- I - under the influence of a force load, the body settles (becomes shorter) by 30% or less;
- II - by 30-50%;
- III - 50% or more.
Compression fractures usually involve one vertebra (very rarely several). Violations are observed only in his body. Usually, injury occurs when falling on the fifth point or on the extended lower limbs. With the compression type, complete diagnostics are required, since it is often accompanied by a fracture of the calcaneus or pelvic bones.

© Artemida-psy - stock.adobe.com. Types of compression fracture
The fragmented type is characterized by the entry of the anterior wall of the vertebra into the body located below. This injury is much more serious than the previous type because:
- the intervertebral disc can split into 2 or more parts;
- the fragment is displaced from back to front (sometimes only back), which leads to damage to the central nervous system located in the spinal canal.
With fracture dislocation, the upper sections are displaced forward. It may be accompanied by:
- displacement of adjacent vertebrae;
- fracture of bone processes and arches.

© Artemida-psy - stock.adobe.com. Vertebral displacement options for rotational fracture
The pathological condition provokes undesirable consequences for the structures of the nervous system (NS):
- squeezing them of varying strength;
- bruise or rupture of nerve endings, spinal cord injury.
Damage is subdivided into:
- uncomplicated (NS are not damaged);
- complicated (there was compression, destruction, rupture of the NS).
Division by pathogenesis:
- traumatic;
- pathological.
The first type is observed after a blow, a fall. A pathological type develops with an already existing disease, which has led to a weakening of tissues. This usually occurs against the background of the following diseases:
- benign or malignant tumor;
- osteoporosis;
- tuberculosis of the bones;
- osteomyelitis.
The pathological type can develop with the slightest load on the lumbar region. Sometimes even your own body weight is enough.
Symptoms
In case of injury, the following clinical picture is observed:
- pain syndrome;
- stiffness of movements;
- prolonged tension of the back muscles;
- swelling in the area of damage.
Pain can be characterized as follows:
| Factor | Description |
| Localization | Fracture site. |
| Spread | May transfer to surrounding tissues. |
| Character | Aching. |
| Expressiveness | Medium to strong. Painful sensations increase with movement. |
| Time of occurrence | Most often at the time of injury. But they may not appear immediately, but several hours after damage. |
Limited movement occurs due to:
- blockage by a splinter of a vertebra;
- damage to the nerve endings responsible for motor function;
- experiencing severe pain by the patient (he reflexively tries not to move in order to avoid unpleasant sensations).
Muscle tension and swelling are the body's natural response to injury.
Sometimes (regardless of whether other structures have suffered or not), the following symptoms may occur:
- flatulence;
- constipation;
- feeling of nausea;
- vomiting, after which the condition does not improve.
With the defeat of the NS, the following symptoms are observed:
- decrease or loss of sensitivity;
- strengthening or weakening of reflexes;
- muscle weakness below the area of injury (sometimes paralysis is possible);
- problems with urination.
With the compression type, the symptoms are blurred. Often the patient does not even pay attention to her and does not make an appointment with the doctor. Pathology is usually detected by chance.
In the pathological type, provoked by osteoporosis, multiple, already fused fractures are often found. This causes deformation of the spinal column, up to the formation of a hump.
With comminuted fractures, the signs listed above are observed. However, the symptoms are more pronounced.

© Photographee.eu - stock.adobe.com
Emergency help
It is very important to get first aid right after injury. The success of further treatment depends on this. Correct action will reduce the likelihood of complications and increase the chances of a favorable outcome.
First of all, you need to call an ambulance. Before the arrival of the victim, put in a horizontal position on a hard, flat surface. Place a low pillow under the head, and a roller under the lower back (it can be made from towels).
In severe injuries, the patient may not be able to feel the lower body. He experiences a painful shock, loses consciousness, vomits. It is very important that the escaping masses do not get into the respiratory tract and the person does not choke on them. To prevent this, the victim must be gently turned to one side and fixed in this position with pillows.
A splint must be applied to the injury site. To alleviate the condition, give the pain relievers available in the home medicine cabinet. It is advisable to apply ice or something cold to the damage. You can only move the patient on a rigid stretcher or board.
All treatments
If the bones are not displaced and the spinal cord is not affected, then conservative therapy is prescribed. It is aimed at restoring motor function without pain and discomfort, restoring the natural position of the spine. Step by step actions:
- Rest on an orthopedic bed.
- Lumbar block with pain-relieving injections.
- Taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics.
- Prescription of medications containing calcium.
- Traction of bones.
- Raising the leg of the bed by 30 °.
- Fixing a weight of 14 kg on the heel or shin.
- Pulling out pathologically altered areas.
- Putting on a corset (5 weeks after the start of treatment).
- The appointment of vertebroplasty (the damaged vertebra is fixed with medical cement, this speeds up the recovery process). Manipulation is permissible only in the absence of displacement of the intervertebral discs.
Corset
Put on for fixation, load distribution. It is made individually for each patient, taking into account the characteristics of the figure.

© Andriy Petrenko - stock.adobe.com
Exercise therapy and massage
Physiotherapy is a method of treatment that is prescribed after conservative therapy or surgery.
To quickly return to normal life, you need to strictly follow all the doctor's recommendations, do exercises daily.
In the absence of severe pain syndrome, exercise therapy is prescribed for 3-5 days of treatment:
- Static and breathing exercises. This takes several weeks.

© Photo_Ma - stock.adobe.com
- In the first week, you can move your legs while lying on the bed. The heels do not come off, one leg moves alternately. You cannot keep a straight leg!
© AntonioDiaz - stock.adobe.com
If at the end of the first week the patient can lift a straight leg for 15 seconds and does not feel pain, then he is on the mend.
- After two weeks, turns to the stomach are allowed. Under the supervision of a doctor, a roller is placed under the chest and feet (10-15 cm in the second case). In this position, the patient lies from 20 to 30 minutes 2-3 times a day.
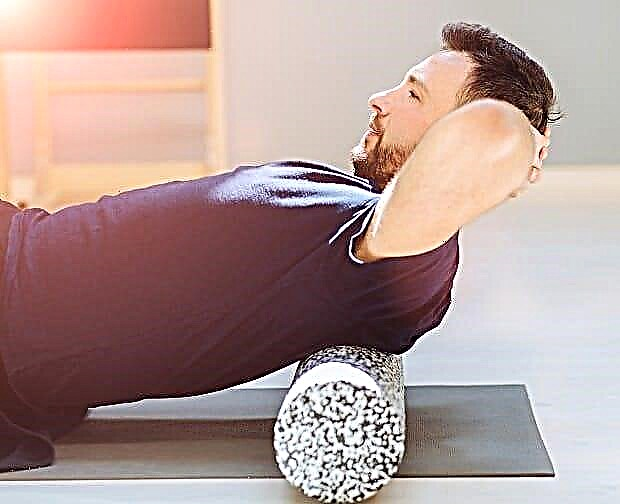

© Iryna - stock.adobe.com
- After three to four weeks, you can do the bike alternately with each leg. Other exercises with raising the legs while lying on the back or stomach are allowed.
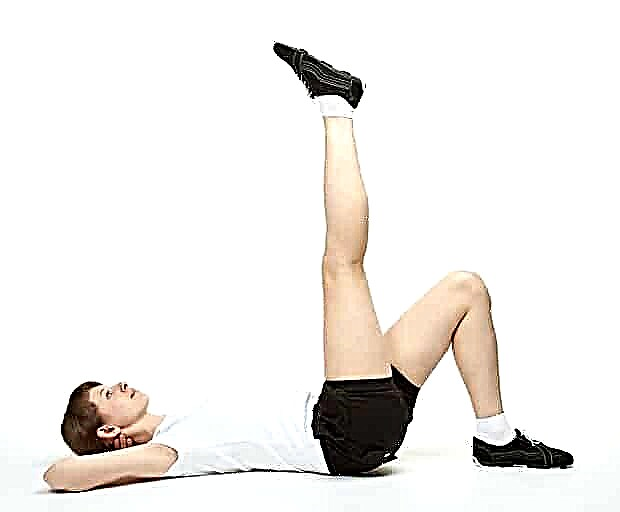

© zest_marina - stock.adobe.com
- At the last stage, it is allowed to rise from the kneeling position (you cannot rise from a sitting position!). Walking is permissible without undue stress on the legs. All movements are aimed at strengthening the muscles of the lower extremities, weakened during prolonged rest. Leaning forward is allowed only 3.5 months after the start of walking. Also, classes in the pool are recommended for a speedy recovery.
In order for the exercises to be beneficial, you must follow simple rules:
- do it daily;
- do each approach efficiently, without being lazy;
- correctly distribute the load (its lack will lead to a lack of effectiveness of actions, and an excess can worsen the condition).
If you overload yourself with exercise, the following complications may develop:
- slowing down or stopping tissue repair;
- loosening of the vertebrae;
- hernia;
- osteoporosis;
- neuralgia;
- paralysis of the lower extremities;
- urinary incontinence;
- violation of reproductive function.
In the initial stages, a quarter of an hour a day is allocated for exercise. Gradually increase the time to 60 minutes, adhere to the daily routine:
- charging;
- afternoon walk;
- five-minute exercise;
- classes in a special group of exercise therapy, gym, swimming pool.
The purpose of the therapeutic massage is to improve blood circulation and strengthen muscles. It also prevents the development of complications. The procedure relieves paresis and paralysis, restores efficiency.

© Microgen - stock.adobe.com
Operative intervention
If the vertebrae are not displaced, kyphoplasty is performed: through small incisions, balloons are fixed to fix the vertebral body. The affected area is filled with bone cement. This minimally invasive operation is prescribed to improve the patient's condition, prevent repeated destruction of the integrity of the vertebrae. Surgical intervention is performed under general anesthesia and does not require a long stay in a hospital.
Kyphoplasty has the following advantages:
- pain passes;
- correct posture is restored;
- complications do not develop;
- almost invisible scars remain;
- you can recover at home;
- the vertebrae become stronger;
- a compression fracture is completely healed if there is no displacement of the discs.
Step by step operation:
- Disinfection of the operated area.
- Local anesthetic injection.
- Insert a special tube into the incision.
- Taking a tissue sample for examination.
- Placing a deflated balloon.
- Filling it with air or liquid.
- Removing the balloon.
- Filling the emerging voids with cement.

© dissoid - stock.adobe.com. Kyphoplasty
Surgical intervention is also indicated for severe lesions. In the process, bone fragments are removed, necrotic tissues are excised, and a prosthesis is implanted if necessary. Titanium plates are often used.
After the operation, it is necessary to wear a corset for about 2 months.
Rehabilitation
After the surgical impact, special attention should be paid to the rehabilitation period. It is very important to follow all the instructions of the attending physician, because further full-fledged existence depends on it. After the operation, the following are prescribed:
- massage;
- electrotherapy;
- ultrasound;
- paraffin applications;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- balneological manipulations.
Complications
The development of such complications is possible:
- Compression of the vascular bed. As a result, there is numbness in the areas that fed this channel.
- Pinching of nerve endings, leading to a violation of the passage of impulses. Because of this, the patient's movements are limited.
- Kyphotic deformities, hump formation. This not only spoils the appearance, but also negatively affects the work of nearby organs.
- Circulatory disorders, because after injury, the patient was motionless for a long time. Because of this, bedsores are formed, soft tissues die off.
- Pelvic problems: urinary incontinence, prolapse of the uterus, impotence.
- Loss of motor functions (a person can become disabled).
In severe cases, a person will no longer be able to return to his usual life. Therefore, you need to be very careful: avoid falls, blows on the back. At the slightest suspicion of injury, immediately contact the clinic for diagnosis.