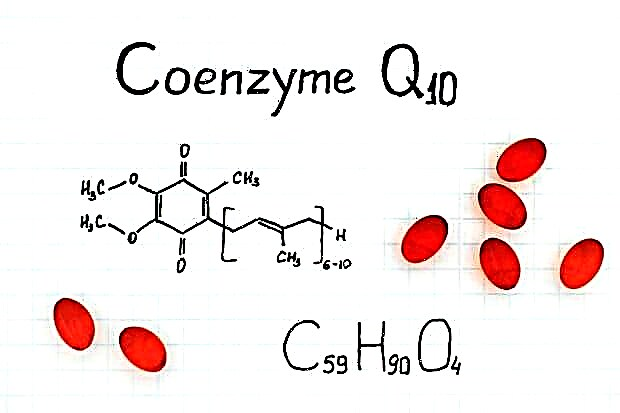
Coenzymes are non-protein organic compounds that are essential for the functioning of many enzymes. Most of them are derived from vitamins.
The reason for metabolic disorders and a decrease in the synthesis of useful substances in the body is often a decrease in the activity of certain types of enzymes. Therefore, coenzymes are so necessary for us.
In a narrow sense, coenzyme is coenzyme Q10, a derivative of folic acid and several other vitamins. Of great importance for the human body are those coenzymes that are produced by the B vitamins.
© rosinka79 - stock.adobe.com
Coenzyme is needed to increase the productivity of cellular energy, which is needed to maintain life. Any process that takes place in the human body requires a colossal energy resource, be it mental activity, the work of the cardiovascular or digestive system, physical activity with a load on the musculoskeletal system. Thanks to the reaction in which coenzymes enter with enzymes, the necessary energy is produced.
Functions of coenzymes
Coenzymes are non-proteinaceous compounds that help activate enzyme potential. They perform 2 main functions:
- Participate in catalytic processes. The coenzyme by itself does not cause the necessary molecular transformations in the body; it enters into the composition of enzymes together with the apoenzyme, and only when they interact, catalytic processes of substrate binding occur.
- Transport function. The coenzyme combines with the substrate, resulting in a strong transport channel through which molecules move freely to the center of another enzyme.
All coenzymes have one important property in common - they are thermally stable compounds, but their chemical reactions are quite different.
Classification of coenzymes
According to the methods of interaction with the apoenzyme, coenzymes are divided into:
- Soluble - during the reaction, it combines with an enzyme molecule, after which it changes in chemical composition and is released again.
- Prosthetic - firmly associated with the apoenzyme, during the reaction it is in the active center of the enzyme. Their regeneration occurs when interacting with another coenzyme or substrate.
According to their chemical structure, coenzymes are divided into three groups:
- aliphatic (glutathione, lipoic acid, etc.)
- heterocyclic (pyridoxal phosphate, tetrahydrofolic acid, nucleoside phosphates and their derivatives (CoA, FMN, FAD, NAD, etc.), metalloporphyrin hemes, etc.
- aromatic (ubiquinones).
Functionally, there are two groups of coenzymes:
- redox,
- group transfer coenzymes.
Coenzymes in sports pharmacology
With intense physical activity, a large amount of energy is consumed, its supply in the body is depleted, and many vitamins and nutrients are consumed much faster than they are produced. Athletes experience physical weakness, nervous exhaustion, and lack of strength. In order to help avoid many symptoms, special preparations with coenzymes in the composition have been developed. Their spectrum of action is very wide, they are prescribed not only to athletes, but also to people with quite serious diseases.
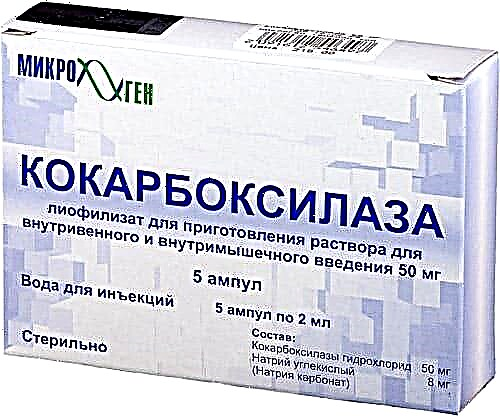
Cocarboxylase
Coenzyme, which is formed only from thiamine entering the body. In athletes, it serves as a means of preventing myocardial overstrain and disorders of the nervous system. The drug is prescribed for radiculitis, neuritis, and acute liver failure. It is administered intravenously, a single dose should not be less than 100 mg.
Cobamamide
Replaces the functional of vitamin B12, is an anabolic. Helps athletes build muscle mass, increases endurance, promotes quick recovery after exercise. Available in the form of tablets and solutions for intravenous administration, the daily rate is 3 tablets or 1000 mcg. The duration of the course is no more than 20 days.

Oxycobalamin
Its action is similar to vitamin B12, but it stays in the blood much longer and is much more quickly converted into a coenzyme formula due to its strong connection with plasma proteins.
Pyridoxal phosphate
The preparation has all the properties of vitamin B6. It differs from it in a quick therapeutic effect, it is prescribed for admission even if pyridoxine phosphorylation is impaired. It is taken three times a day, the daily dose is no more than 0.06 g, and the course is no longer than a month.

Pyriditol
It activates metabolic processes of the central nervous system, increases the permeability of glucose, prevents excessive formation of lactic acid, increases the protective properties of tissues, including resistance to hypoxia, which occurs during intense sports training. The drug is taken three times a day, 0.1 g. after breakfast for a month
Pantogam
It is a homologue of pantothenic acid, accelerates metabolic processes, reduces the manifestation of pain reactions, increases the resistance of cells to hypoxia. The action of the drug is aimed at activating the work of the brain, increasing endurance, it is indicated for use in traumatic brain injuries of various types. Tablets are taken within a month, 0.5 g, no more than three times a day.
Carnitine
It is produced in the form of an injection drug, the action of which is aimed at activating fat metabolism, accelerating cell regeneration. It has anabolic, antihypoxic and antithyroid effects. It is a synthetic substitute for vitamin B6. Effective as an intravenous drip.

Flavinate
It is formed in the body from riboflavin and is actively involved in carbohydrate, lipid and amino acid metabolism. It is produced in the form of a solution for intramuscular injections, since its absorption in the stomach is ineffective in violation of riboflavin absorption.
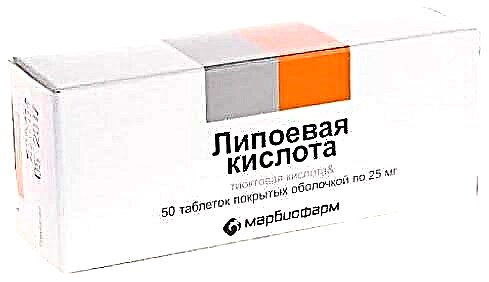
Lipoic acid
Normalizes carbohydrate metabolism. Increases the rate of oxidation of carbohydrates and fatty acids, which contributes to an increase in energy reserves.