The legs are the support for the body, and the feet are the support for the legs. Often, athletes underestimate the importance of a healthy foot and ankle in achieving optimal athletic performance, not to mention overall wellness and health. The most unpleasant thing is that even minor injuries to the foot and ankle can have very bad long-term consequences for health in the future. How foot injuries occur, what is foot dislocation and how to recognize, prevent and treat it - we will tell you in this article.
Foot structure
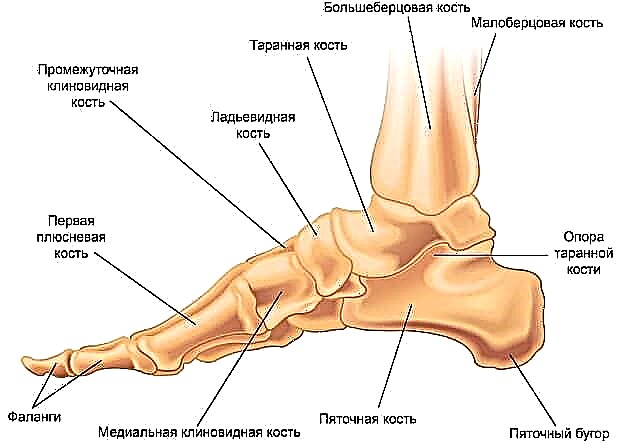
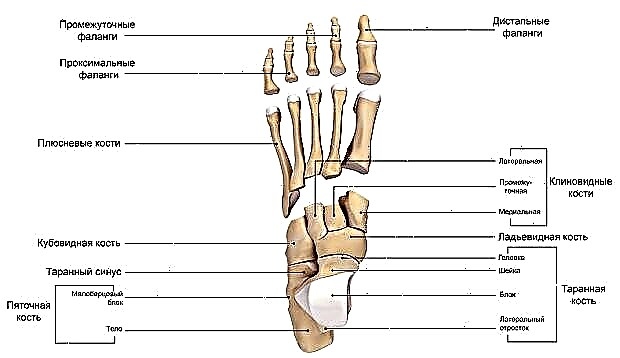
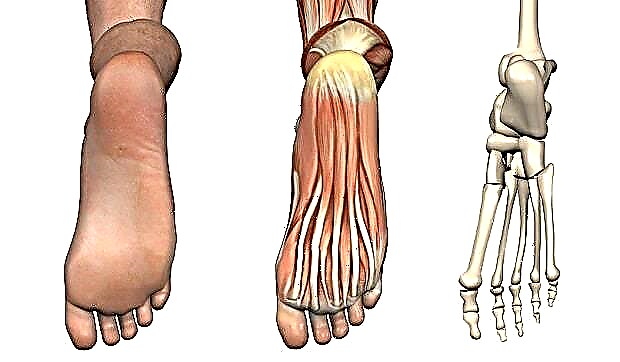
The foot is a complex anatomical formation. It is based on a bony frame, represented by the talus, calcaneus, scaphoid, cuboid and sphenoid bones (tarsal complex), bones of the metatarsus and fingers.
Bone base
- The talus serves as a kind of "adapter" between the foot and the lower leg, due to its shape, providing mobility of the ankle joint. It lies directly on the heel bone.
- The heel bone is the largest forming the foot. It is also an important bone landmark and an attachment point for the tendons of the muscles and the aponeurosis of the foot. In functional terms, it performs a supporting function when walking. In front, in contact with the cuboid bone.
- The cuboid bone forms the lateral edge of the tarsal part of the foot, the 3rd and 4th metatarsal bones are directly adjacent to it. With its medial edge, the described bone is in contact with the scaphoid bone.
- The scaphoid bone forms the medial part of the tarsal part of the foot. Lies in front and medial to the calcaneus. In front, the scaphoid bone is in contact with the sphenoid bones - lateral, medial and medial. Together they form the bony base for the metatarsal bones.
- The metatarsal bones are related in shape to the so-called tubular bones. On the one hand, they are motionlessly connected to the bones of the tarsus, on the other, they form movable joints with the toes.
© rob3000 - stock.adobe.com
There are five toes, four of them (from the second to the fifth) have three short phalanges, the first has only two. Looking ahead, the toes play an important role in the gait pattern: the final stage of pushing the foot off the ground is only possible with the first and second toes.
© 7activestudio - stock.adobe.com
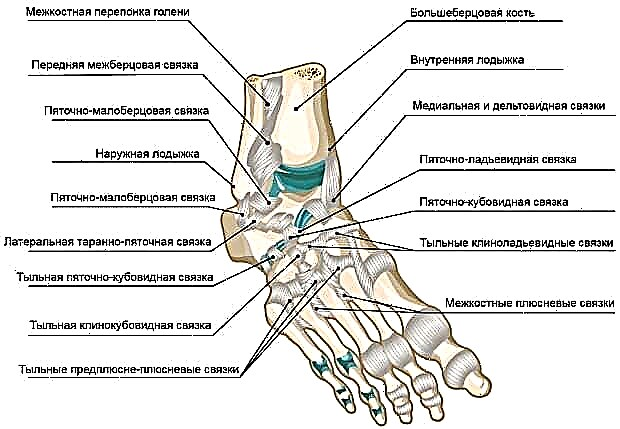
Ligamentous apparatus
The listed bones are strengthened by the ligamentous apparatus, they form the following joints among themselves:
- Subtalar - between the talus and calcaneus. It is easily injured when the ankle ligaments are stretched, with the formation of subluxation.
- Talocalcaneonavicular - around the axis of this joint it is possible to perform pronation and supination of the foot.
- In addition, it is important to note the tarsometatarsal, intermetatarsal and interphalangeal joints of the foot.
© p6m5 - stock.adobe.com
The muscles located on the plantar side of the lower leg are the most significant for the formation of the correct calf arch. They are divided into three groups:
- outdoor;
- internal;
- average.
The first group serves the little finger, the second group serves the thumb (responsible for flexion and adduction). The middle muscle group is responsible for flexion of the second, third and fourth toes.
Biomechanically, the foot is designed in such a way that, with the correct muscle tone, its plantar surface forms several arches:
- external longitudinal vault - passes through a mentally drawn line between the calcaneal tubercle and the distal head of the fifth phalangeal bone;
- internal longitudinal arch - passes through a mentally drawn line between the calcaneal tuberosity and the distal head of the first metatarsal bone;
- transverse longitudinal arch - passes through a mentally drawn line between the distal heads of the first and fifth metatarsal bones.
In addition to muscles, a powerful plantar aponeurosis, mentioned somewhat above, is involved in the formation of such a structure.
© AlienCat - stock.adobe.com
Types of dislocation of the foot
Dislocations of the foot can be divided into three types:
Subtalar dislocations of the foot
With this type of foot injury, the talus remains in place, and the adjacent calcaneal, scaphoid and cuboid, as it were, diverge. In this case, there is a significant trauma to the soft tissues of the joint, with damage to the blood vessels. The joint cavity and periarticular tissues are filled with an extensive hematoma. This leads to significant swelling, pain and, which is the most dangerous factor, to impaired blood delivery to the limb. The latter circumstance can serve as a trigger for the development of foot gangrene.
Dislocation of the transverse tarsal joint
This type of foot injury occurs with direct trauma. The foot has a characteristic appearance - it is deployed inward, the skin on the back of the foot is stretched. When palpating the joint, the inwardly displaced scaphoid is clearly felt. The edema is as pronounced as in the previous case.
Dislocation of the metatarsal joint
A fairly rare foot injury. Most often occurs with direct injury to the front edge of the foot. The most likely mechanism of injury is landing from an elevation on the toes. In this case, the first or fifth phalangeal bones can be displaced in isolation, or all five at once. Clinically, there is a step-like deformity of the foot, edema, and the inability to step on the foot. Voluntary movements of the toes are significantly difficult.
Sprained toes
The most common dislocation occurs in the metatarsophalangeal joint of the first toe. In this case, the finger moves inward or outward, with simultaneous flexion. The injury is accompanied by pain, significant painful sensations when trying to push off the ground with the injured leg. Wearing shoes is difficult, often impossible.

© caluian - stock.adobe.com
Dislocation signs and symptoms
The main symptoms of a dislocated foot are:
- Pain, which arises sharply, immediately after the impact of a traumatic factor on the foot. In this case, after the cessation of exposure, the pain persists. Strengthening it occurs when you try to lean on the injured limb.
- Edema... The area of the damaged joint increases in volume, the skin is stretched. There is a feeling of expansion of the joint from the inside. This circumstance is associated with concomitant injury of soft tissue formations, in particular, vessels.
- Loss of function... It is impossible to make a voluntary movement in the damaged joint; an attempt to do this brings significant painful sensations.
- Forced position of the foot - part or all of the foot is in an unnatural position.
Be careful and attentive! It is impossible to distinguish a dislocation of the foot from a stretch and fracture of the foot visually, without having an X-ray machine.
© irinashamanaeva - stock.adobe.com
First aid for dislocation
First aid for dislocated foot consists in the following algorithm of actions:
- Place the victim on a comfortable, level surface.
- Next, you should give the injured limb an elevated position (the foot should be above the knee and hip joints), placing a pillow, jacket or any suitable means under it.
- To reduce post-traumatic edema, the injury must be cooled. For this, ice or any product frozen in the freezer (for example, a pack of dumplings) is suitable.
- If the skin is damaged, it is necessary to apply an aseptic dressing to the wound.
- After all the actions described above, you need to take the victim to a medical facility as soon as possible, where there is a traumatologist and an X-ray machine.
Dislocation treatment
Dislocation treatment consists in the procedure of setting the leg and giving it a natural position. Reduction can be closed - without surgical intervention, and open, that is, through an operative incision.
It is impossible to give any specific advice on what and how to treat a dislocated foot at home, since you cannot do without the help of an experienced traumatologist. Having corrected the dislocation, he can give you some recommendations on what to do when the foot is dislocated to restore motor function as soon as possible.
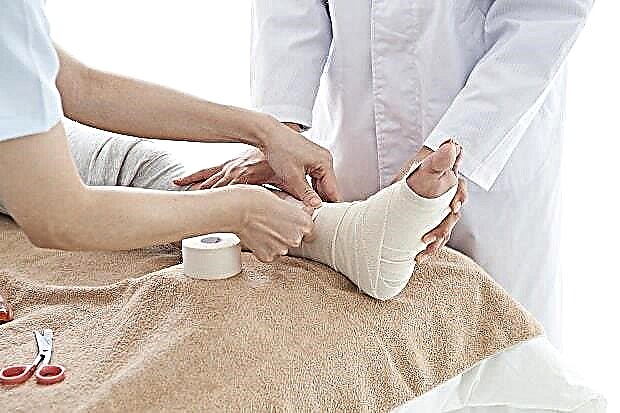
After the reduction procedures, a fixation bandage is applied, for a period of four weeks to two months. Do not be surprised that when fixing the lower leg, the splint will be applied up to the lower third of the thigh - with the knee joint fixed. This is a necessary condition, since the process of walking with a fixed ankle is very dangerous for the knee joint.
© Monet - stock.adobe.com
Dislocation recovery
After removing the immobilization, the rehabilitation process begins - the gradual inclusion of the muscles of the immobilized limb in the work. You should start with active movements, but without support on the injured limb.
To restore bone density at the site of injury, you need to walk a short distance every day, increasing it step by step.
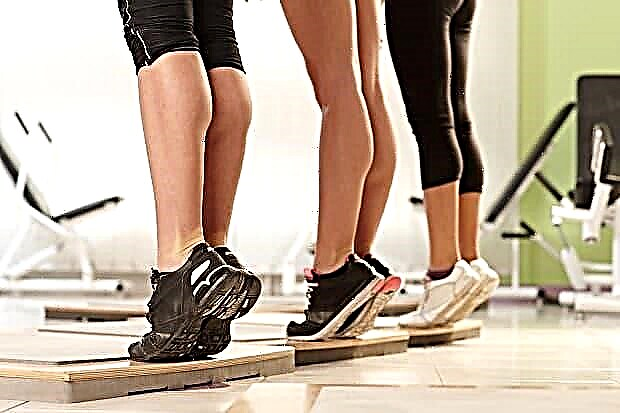
For a more active restoration of limb mobility, we offer several effective exercises. To perform them, you will need a cuff with a fixation ring and a strap for attaching to the Achilles tendon. We put the cuff on the projection area of the metatarsal bones. We fix the strap across the Achilles tendon just above the heel. We lie down on the mat, put our shins on the gymnastic bench. Three options follow:
- We become buttocks close to the block device. We attach a small weight (no more than 10 kg) to the fixing ring from the lower block. We perform flexion in the ankle joint until a strong burning sensation is felt in the front of the lower leg.
- We stand sideways to the block device (the block should be located on the side of the thumb). We fasten the weights (no more than 5 kg) and pronate the foot. Next, we change the position so that the block is on the side of the little finger and begin to perform supination. The weight of the weights are the same as when pronating.
- The next exercise is toes. Can be performed from a standing position on the floor, standing on a dais, or from a sitting position. In the latter case, the knees and hip joints should be bent at an angle of 90 degrees, the feet should be on the floor. You can put a small weight on your knees. We carry out a forward rise on toes with the heels off the floor.

© nyul - stock.adobe.com
In addition to the described exercises for developing the foot after an injury at home, you can use other methods and improvised means: roll a ball with your foot, perform backbends with a towel, and more.