Most people are familiar with the concept of cardio in one way or another. Consider the features and types of such training, the relationship between loads and the pulse, the benefits of exercise for weight loss and for the heart.
What is cardio workout?
What does cardio training mean? It is synonymous with aerobic exercise, in which the heart is actively working and energy is produced due to the oxidation of glucose molecules with oxygen. The general nature of the training is a fairly high intensity of the muscular, cardiovascular and respiratory systems with a minimum strength load. The term comes from the Greek kardia - heart.
The opinion that strength training cannot be aerobic is wrong. Any exercise that raises your heart rate and forces you to breathe actively in the process is referred to as cardio. But then, what is the difference between cardio training and strength training? Resistance training to increase muscle mass or strength is anaerobic exercise. In other words, exercises in which glycolysis in the muscles occurs without the participation of oxygen. This also happens when the heart rate is too high - from 80% of the athlete's maximum.
The relationship of cardio and heart rate
The most important indicator of training intensity is heart rate (heart rate - heart rate). For classes to be beneficial, not harmful, it is necessary to constantly monitor the heartbeat.
Note! The load is selected so that the pulse does not go beyond a certain range. Without reaching the lower limit of heart rate, athletes get a weak effect. Going beyond the upper limit, those involved in the risk of health (primarily, heart).
The heart rate range for aerobic exercise is calculated by the formulas:
- lower limit = MHR x 0.6;
- upper limit = MHR x 0.8.
Where MHR is the maximum heart rate. The calculation of the maximum is different for men and women and is done using several formulas. The general and most commonly used are:
- for men = 220 - age in years;
- for women = 226 - age in years.
The following formulas have been recognized as more accurate in recent years:
- for men = 208 - 0.7 x age in years (Tanaka formula);
- for women = 206 - 0.88 x age in years (Martha Gulati's formula).
For example, if a man is 30 years old, then the training load on the heart should be within the range of 112-150 beats per minute. The ceiling of the heart rate in this case is 187 beats per minute. For a woman of the same age, the range will be 108-144, and the MHR - 180.
These are general calculations that do not take into account the training of the athlete, his state of health at a particular moment, the presence or absence of chronic diseases. The calculations are valid for the average person.
Benefits of cardio workouts
Let's figure out what cardio is for.
For the body in general
For the body, the benefits of regular cardio workouts are obvious:
- Improving heart function... The heart muscle should be tense in the same way as the others. Regular and controlled increase in load leads to an improvement in the process of pumping blood and a decrease in heart rate at rest.
- Lung health... Thanks to cardio loads, the muscles involved in the breathing process are strengthened. As a result, the work of the lungs becomes easier - it becomes easier to breathe.
- Improving blood pressure... Aerobic training increases the number of red blood cells that provide oxygen transport. Exercise lowers cholesterol levels, helps burn calories, and maintains normal blood vessels.
- Improving metabolism... Exercise increases your metabolic rate. This responds to the rapid melting of accumulated fatty deposits and the prevention of new stores.
- Improving hormonal levels... Aerobic training promotes the production of hormones that prevent the onset of depression. It becomes easier to live psychologically - it is easier for a trained person to endure stress.
- Deep sleep... People who practice regular cardio fall asleep faster. In addition, their sleep is deeper and better - due to the balance of sleep phases, the body is fully restored.
- Improving bone health... Half-hour cardio several times a week increases bone density. This is especially true for the elderly. A very common cause of hospitalization is a hip fracture. Strong bones improve sad statistics.
- Prevention of diabetes... Aerobic exercise improves the ability of muscle tissue to process glucose. Thanks to exercise, the blood sugar level is maintained at the proper level - the number and amplitude of its jumps decreases.
- Increased endurance... For many athletes, this is the main reason. Cardio training increases the body's ability to store energy and use it sparingly.

© nd3000 - stock.adobe.com
When losing weight
The mechanism of weight loss is based, first of all, on the body's ability to store energy quickly. The body takes such energy from carbohydrates and stores it in the form of glycogen. To begin to melt fat, you must first use up glycogen, which is stored in the muscles and liver.
For this reason, effective cardio training should be either long-term or intense (interval). In a fat-burning context, it is best to give yourself an aerobic load immediately after anaerobic - after strength training, where glycogen is depleted. Another good option is in the morning on an empty stomach, when glycogen stores are also depleted.
Example. Many run regularly. But their run lasts 20-30 minutes. Jogging intensity is low. During this time, the body manages to deplete glycogen stores, but does not have time to get to fat. With the first meal, glycogen stores are replenished. To get the fat burning effect, you need to jog for at least 40-50 minutes.
With any cardio exercise, it is imperative to eat right. Without a calorie deficit, you cannot get a lean body. Yes, deficiency is theoretically possible with an illiterate diet. But at the same time, it will be quite difficult to count, and it will also be very likely a constant feeling of hunger, since if the entire diet consists of fast food or sweets, it will be small. With a healthy diet high in protein and complex carbohydrates, you'll be full all day and full of energy.
Important! Cardio training and proper nutrition go hand in hand.
What does science say?
Which is more effective - cardio or strength training? A group of researchers gathered experimental subjects and divided them into 4 groups:
- control;
- doing 30 minutes of walking 5 days a week;
- exercising for half an hour on simulators 5 days a week;
- mixed - those who practiced 15 minutes of strength training and 15 minutes of aerobic training (also 5 days a week).
The experiment lasted 12 weeks. The best results were shown by groups 4 and 3 - minus 4.4% and 3% fat, respectively. Strength and combination training proved to be more effective than pure cardio. You can read more about the study here.
No less interesting is the study comparing the effectiveness of aerobic exercise and diet. This experiment, which lasted about a year, involved over 400 women. As in the previous case, the participants were divided into 4 groups:
- practicing diet;
- doing 45 minutes of light cardio 5 days a week;
- combined;
- control.
Results: a year later, fat loss in the 1st group was 8.5%, in the 2nd - 2.5%, in the 3rd - 10.8%. That is, diet and a combination of proper nutrition and aerobic exercise were the most effective strategies. But what is pure cardio? Cardio itself leads to minimal fat loss. If, at the same time, during the day you have a surplus of calories, you can completely forget about losing weight in the long term.
Let's make a reservation that the experimental loads were moderate. If the training had been less gentle, the results would probably be different. But in any case, research shows that combining exercise with diet is more effective. Read more about the experiment here.

© baranq - stock.adobe.com
Types of cardio workouts
There are many types of aerobic workouts - from running to dancing and fiddling in the garden. Most popular options:
- walking, including on a treadmill;
- low and medium intensity running;
- swimming;
- a ride on the bicycle;
- circuit training;
- step aerobics;
- jumping rope;
- lessons on the orbit track.
Do not forget to make sure that the pulse does not go into the anaerobic zone (over 80% of the MHR). This indicator is quite easy to achieve for poorly trained people with, for example, intense circuit training.
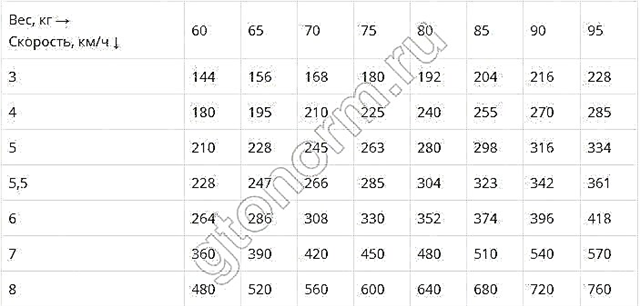
The relationship of various types of cardio with calorie loss is shown in the table (indicators in kcal, burned in 30 minutes):
| Cardio type | With a weight of an athlete of 55 kg | With an athlete weighing 70 kg | With an athlete weighing 85 kg |
| Running (10 km / h) | 375 | 465 | 555 |
| Jumping rope | 300 | 372 | 444 |
| Exercise bike | 210 | 260 | 311 |
| Step aerobics | 210 | 260 | 311 |
| Ellipsoid | 270 | 335 | 400 |
| Rowing machine | 210 | 260 | 311 |
| Swimming | 300 | 372 | 444 |
| Slow aerobics | 165 | 205 | 244 |
| Intensive aerobics | 210 | 260 | 311 |
| Crossfit | 240 | 298 | 355 |
| Water aerobics | 120 | 149 | 178 |
| Hatha yoga | 120 | 149 | 178 |
| Walking at a calm pace (4 km / h) | 83 | 105 | 127 |
| Walking at an energetic pace (6 km / h) | 121 | 154 | 187 |
| Circular training | 220 | 280 | 340 |
Which workout to choose?
The choice depends on the initial state of the person and the tasks that he sets for himself. The most popular option is running. But it is not suitable for those who suffer from too pronounced obesity. Heavy weight puts pressure on the knees - after a while, serious problems are likely to appear.
Regardless of potential problems, the choice should be based on the effectiveness of the training, as shown in the table above. The most effective options listed are jogging, ellipsoid, swimming, and jumping rope.
The choice is tied to the capabilities of the students. For various reasons, visiting the gym or jogging in the park is not available to everyone. In this case, home workouts are preferable.

© .shock - stock.adobe.com
Cardio at home
What is important to consider when doing cardio at home? The same aspects as in other cases - tracking the heart rate, accounting for lost calories, taking care of joints. If you don't have a heart rate monitor at hand, you can focus on breathing. If the load is too high, it will go astray - it will be difficult to talk.
The home athlete has a ton of exercises in his arsenal. For instance:
- Running in place is a good alternative to regular running. "Run" with intense trampling from foot to foot, with alternate lifting of the knees, with the heels touching the buttocks - diversify the training.
- Jumping in place - alternate quick, shallow jumps with squat movements.
- Burpee is a crossfit exercise.
- Elements of aerobics and dancing.
It's great if you have an exercise bike at home. Without taking up much space, it will help to cope with excess weight and other problems that are within the "competence" of cardio. The abundance of aerobic exercise leaves no reason to give up cardio loads - you can do it in any conditions.
Contraindications
Cardio training is contraindicated in people who have had a stroke or heart attack. You can not burden the heart and those who suffer from high hypertension. In their case, only light gymnastics.
Before starting to exercise, be sure to take into account the condition of the joints. Herniated discs, sore knees, recent surgeries or fractures are reasons to approach the issue very carefully. Asthmatics and people suffering from obesity should also consult a doctor.
You cannot train when:
- ARVI;
- acute allergies;
- menses;
- stomach ulcer and 12 duodenal ulcer;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases.
In addition, beginners are not allowed to use the intensity with which experienced athletes work. You need to start with light loads, gradually increasing them and your level. In this case, you need to remember about the heart rate range.